Amplifier is the abbreviation of power amplification. In terms of voltage or current amplification, the power amplifier requires a certain, undistorted power, and generally works in a large signal state. Therefore, the power amplifier circuit generally includes a special problem that the voltage amplification or current amplification circuit does not have, and the specific performance is as follows: The power is as large as possible; 2 usually works in a large signal state; 3 nonlinear distortion is prominent; 4 improving efficiency is an important concern; 5 power device safety issues. For audio power amplifier circuits, you need to pay attention to the above problems. French Type Electionics Connection
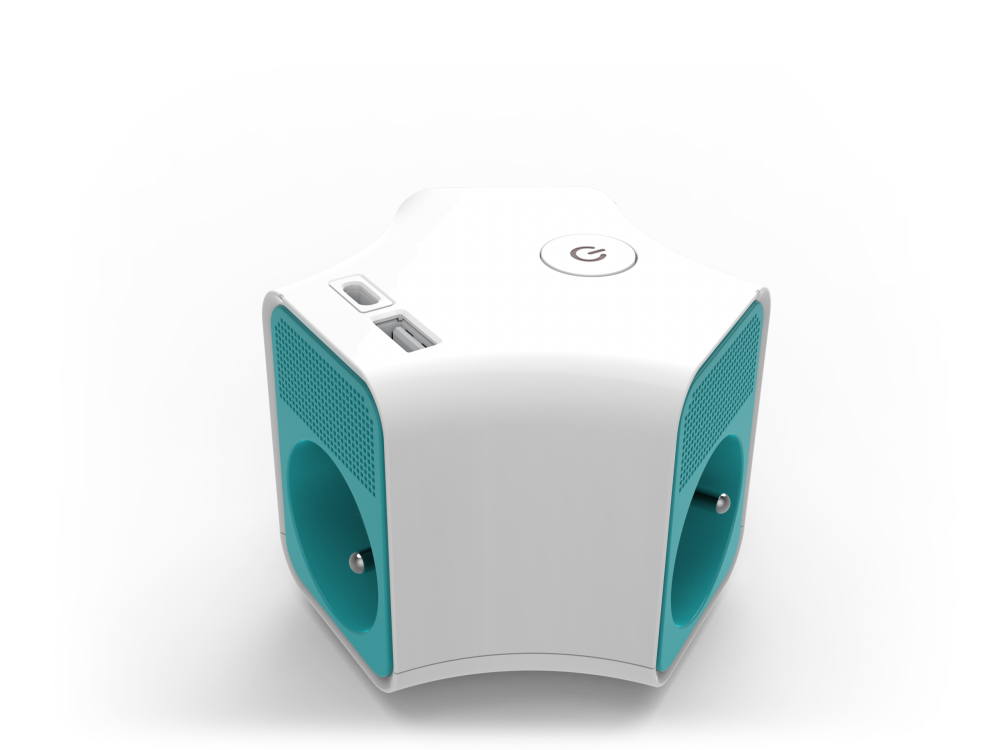
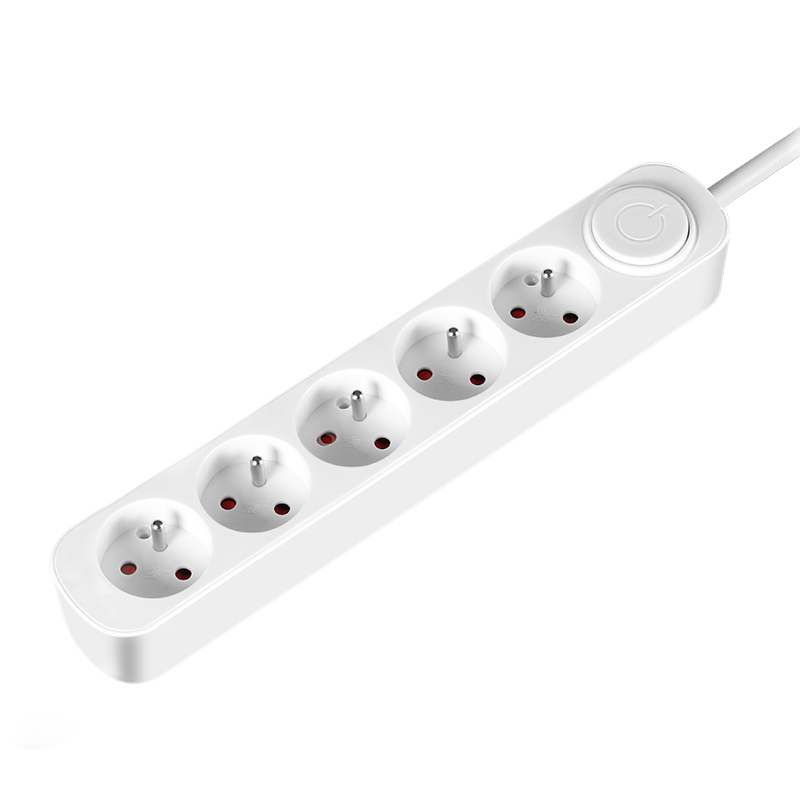
French power strips distribute power to multi devices, computer, refrigerator, etc at same time. The dural plastic housing(flame retadent PP merterial) stands 750 degree high temperature, children safety shutter, premium safety for you and your family. Right-angle plug type E can be flexibility used for suers and save space at same time. The KYFEN French USB power strips with USB type A or type C, deliver power to moblie phone, game machine or other mobile machine. KYFEN French extension cord socket got CE/NF/RoHS/REACH approved, comply with eu sales requirements.
French Type Electionics Connection,Electrical Connector,Electrical Wire Connectors,Power Extension Socket CIXI KYFEN ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD, , https://www.kyfengroup.com
According to the different conductivity modes of the amplifying circuit, the audio power amplifier circuit is classified according to the analog and digital types. The analog audio power amplifier usually has class A, class B, class AB, class G, class H TD power amplifier, and digital circuit power amplifier is divided into class D. , class T. The above detailed description and analysis of the power amplifier circuit are given below.
1. Class A power amplifier (also known as Class A power amplifier) 
Class A power amplifiers, as shown in the figure above, do not exhibit a current-cut (ie, stop output) amplifier for the entire period of the signal. However, Class A amplifiers generate high heat when operating and are inefficient. Although class A power amplifiers have the above drawbacks, the inherent advantage is that there is no crossover distortion, and the internal principle has some innate advantages. It is an ideal choice for replaying music. It can provide very smooth sound quality, and the sound is round and warm, high frequency. Transparent open, the advantages of full and transparent mid-range. Single-ended amplifiers are Class A working methods, and push-pull amplifiers can be Class A or Class B or Class A.
2. Class B power amplifier (also known as Class B power amplifier) 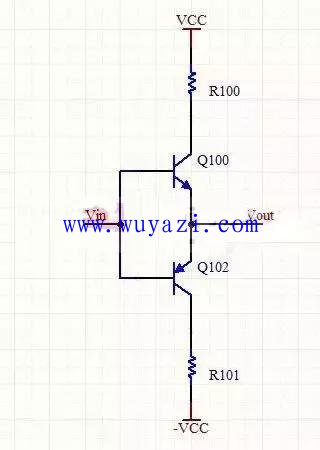
Class B power amplifier refers to a type of amplifier in which the two positive and negative sinusoidal signals are amplified and output by two transistors of the push-pull output stage. The conduction time of each transistor is half a cycle of the signal, which usually produces what we say. The crossover is distorted. This distortion can be reduced or even eliminated as much as possible by adjustment of the analog circuit. Class B amplifiers are significantly more efficient than Class A amplifiers.
3. Class AB power amplifier (also known as Class A and B)
Class AB power amplifiers are between Class A and Class B. Each transistor of push-pull amplification has an on-time greater than half a cycle of the signal and less than one cycle. Therefore, the class AB power amplifier effectively solves the crossover distortion problem of the class B amplifier, and the efficiency is higher than that of the class A amplifier, so it has been widely used. 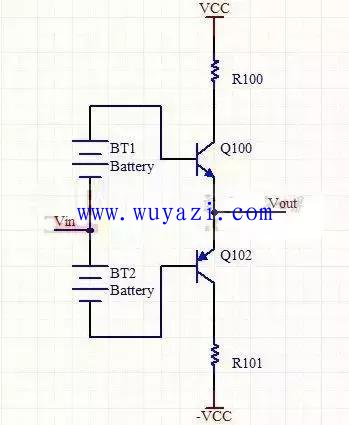
4. Class D power amplifier (also known as Ding amplifier) 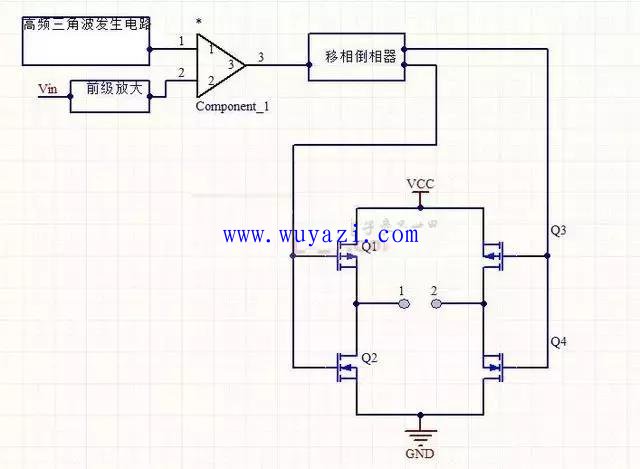
Class D power amplifiers, also known as digital amplifiers, use a very high frequency switching circuit to amplify the audio signal. The specific working principle is as follows: Class D power amplifier adopts asynchronous modulation mode, and the high frequency carrier signal remains when the audio signal period changes. Constant, therefore, when the audio frequency is relatively low, the number of PWM carriers is still high, so it is very advantageous to suppress the high frequency carrier and reduce the distortion, and the frequency conversion band of the carrier has the principle of the audio signal frequency, so there is no basis The problem of mutual interference between waves. Many D-type amplifiers with powers up to 1000W are just as large as VHS tapes. These amplifiers are not suitable for use as broadband amplifiers, but have many applications in active subwoofers.
5, Class G amplifier
Class G amplifiers are an improved form of a multi-supply class AB amplifier. Class G amplifiers take full advantage of the fact that audio has a very high crest factor (10-20dB). Most of the time, the audio signal is at a lower amplitude and will show a higher peak in less time. The figure below is a typical functional block diagram of a Class G amplifier integrated IC. 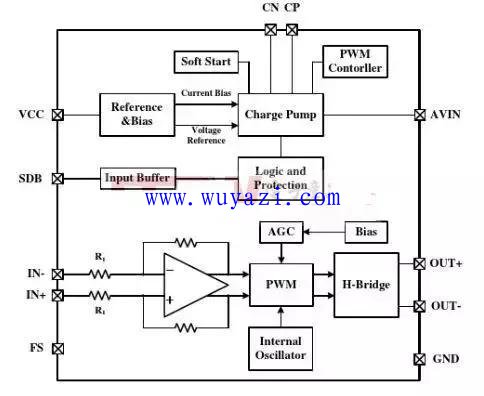
Class G amplifiers use an adaptive power rail and utilize a built-in buck converter to generate the positive supply voltage of the headphone amplifier. The charge pump inverts the amplifier's positive supply voltage and produces the amplifier's negative supply voltage. This allows the headphone amplifier output to be concentrated at 0V. When the amplitude of the audio signal is low, the buck converter produces a low amplifier negative supply voltage. This minimizes the power consumption of Class G amplifiers while playing low-noise, high-fidelity audio, and Class G amplifiers have higher efficiency than traditional Class AB headphone amplifiers.
The amplification principle of this type of power amplifier is the same as that of the class AB power amplifier. One important feature is that the power supply part uses two or more sets of voltages, the low power operation uses low voltage, and the high power automatically switches to high voltage.
6. Class H power amplifier The amplifier circuit of this type of power amplifier has the same principle as the class AB power amplifier, but the power supply part adopts a switching power supply that can adjust multi-level output voltage, and automatically detects the output power to select the power supply voltage.
7, class K power amplifier
Class K power amplifiers integrate an internal bootstrap boost circuit and various power amplifier circuits. Everyone knows that Class D power amplifiers are just one of the most efficient digital power amplifiers in many power amplifier circuits, while Class K power amplifiers are only integrated internally according to needs. The bootstrap boost circuit and the required power amplifier circuit, if the demand efficiency is high, add a class D power amplifier, and if the sound quality is good, add a class AB power amplifier.
8. Class T power amplifier The principle of this type of power amplifier is the same as that of the class D power amplifier, but the signal part adopts DDP technology (the core is the adaptive algorithm and prediction algorithm of small signal). The working principle is as follows: the current of the audio signal entering the speaker is all processed by the DDP to control the conduction or closing of the high-power high-frequency transistor, thereby achieving high-fidelity linear amplification of the audio signal. This type of power amplifier has a class of power amplifiers with high efficiency, low distortion, and sound quality comparable to that of class AB power amplifiers. 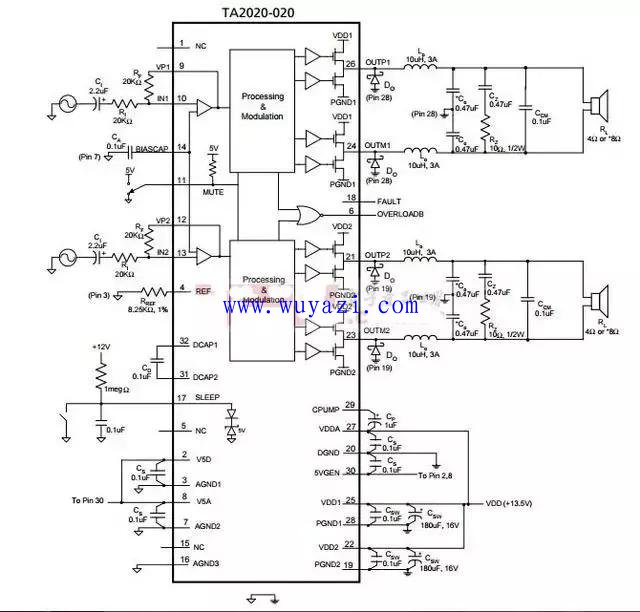
The figure above shows the internal module structure of the TA2020. As can be seen from the above figure, the chip mainly concentrates on processing and modulation modules to achieve high-quality audio characteristics.
9. TD-type power amplifier The amplification part of this type of audio power amplifier is the same as that of the class AB power amplifier, but the power supply part adopts a completely independent adjustable high-precision adjustable stepless output adjustable digital power supply. The voltage progressive value is 0.1V, and the power is automatically detected. To adjust the rise or fall of the voltage. This type of power amplifier needs a high-precision adjustable digital power supply, and needs to be specially designed for the power supply, and cannot be concentrated on one chip. Therefore, such a power amplifier is mainly used in an advanced sound, and the circuit is also complicated.
For the rear class 6, 7, and 9 amplifiers, special power supplies are required, so the functions cannot be concentrated on one IC. For the classic Class A, Class B, Class AB and Class D amplifiers have specialized ICs. In the actual design, various types of power amplifier circuits applied in different fields are needed, and only need to be based on this, plus the corresponding power supply or processing module.