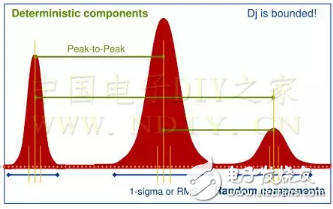
The ITU-T G.701 standard defines jitter as: "Jitter refers to the offset of a significant transient change of a digital signal relative to an ideal position in the short term." There is also a concept similar to jitter, drift. In general, jitter refers to the timing deviation that occurs relatively quickly, and drift refers to the relatively slow timing offset that occurs. The ITU defines the threshold between drift and jitter as 10 Hz, the jitter with an offset frequency greater than 10 Hz, and the drift below 10 Hz. Jitter can be divided into random jitter (RJ) and deterministic jitter (DJ), and deterministic jitter can be divided into periodic jitter (PJ), data-dependent jitter (DDJ) and duty cycle jitter (DCD). As shown below: Abbreviations: TJ: Total Jitter total jitter DJ: DeterminisTIc Jitter deterministic jitter RJ: Random Jitter random jitter PJ: Periodic Jitter periodic jitter DDJ: Data Dependent Jitter data-dependent jitter DCD: Duty Cycle DistorTIon duty cycle jitter TIE: TIme Interval Error time interval error RMS: Root Mean Square Root Mean Square ISI: Inter Symbol Interference 1. Random jitter (RJ) The causes of random jitter are complex and difficult to eliminate. The internal thermal noise of the device, random vibration of the crystal, cosmic rays, etc. may cause random jitter. Random jitter satisfies the Gaussian distribution and is theoretically borderless. As long as the test time is long enough, the random jitter is also infinite. The Gaussian distribution probability density function graph is shown in the figure below. Therefore, the front-front value of random jitter must be expressed in conjunction with the error rate BER. RJRMS = standard deviation of probability density function (pdf): σ, front-front value of random jitter RJpk-pk=N*σ, according to different BER , N is different, as shown below: 2. Deterministic jitter (DJ) Deterministic jitter is not a Gaussian distribution, usually marginal, and it is repeatably predictable. Signal reflection, crosstalk, switching noise, power supply interference, EMI, etc. all produce DJ. The probability density function graph of DJ is shown below: The hand-held Electric Fan is intelligently controlled and adjusted in three gears, and the wind power can be adjusted according to your own needs. The lithium battery of the Rechargeable Fan has strong versatility, recyclable charging, low use cost, simple and elegant appearance, firm structure, small size, light weight and convenience. More unique designs for student travel and outdoor sports bring more comfort to more consumers. Handheld Fan,Portable Hand Fan,Mini Hand Fan,Mini Handheld Fan Dongguan Yuhua Electronic Plastic Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.yuhuaportablefan.com