The baseband chip is used to synthesize the baseband signal to be transmitted or to decode the received baseband signal. Specifically, when transmitting, the audio signal is compiled into a baseband code for transmission; upon reception, the received baseband code is interpreted as an audio signal. At the same time, it is also responsible for the compilation of address information (mobile phone number, website address), text information (short message text, website text), and picture information. composition The baseband chip can be divided into five sub-blocks: a CPU processor, a channel encoder, a digital signal processor, a modem, and an interface module. The CPU processor controls and manages the entire mobile station, including timing control, digital system control, radio frequency control, power saving control, and human-machine interface control. If frequency hopping is used, control of frequency hopping should also be included. At the same time, the CPU processor completes all the software functions of the GSM terminal, namely layer1 (physical layer), layer2 (data link layer), layer3 (network layer), MMI (human-machine interface) and application layer software of the GSM communication protocol. The channel encoder mainly performs channel coding, encryption, and the like of service information and control information, wherein the channel coding includes convolutional coding, FIRE code, parity check code, interleaving, and burst formatting. The digital signal processor mainly performs channel equalization using Viterbi algorithm and speech encoding/decoding based on regular pulse excitation-long-term prediction technology (RPE-LPC). The modulation/demodulator mainly performs the Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) modulation/demodulation method required by the GSM system. The interface part includes three sub-blocks: an analog interface, a digital interface, and a human-machine interface; (1) The analog interface includes: a voice input/output interface; a radio frequency control interface. (2) Auxiliary interface; analog power collection such as battery power and battery temperature. (3) Digital interface includes; system interface; SIM card interface; test interface; EEPROM interface; memory interface; ROM interface is mainly used to connect the memory FLASHROM of the stored program, usually stores layer1, 2, 3, MMI and application layer in FLASHROM program of. The RAM interface is mainly used to connect to a static RAM (SRAM) that stores temporary data. At present, everyone will judge the strength of the signal through the wifi signal cell or mobile phone signal grid displayed on the ipad or mobile phone. However, in fact, the signal strength is very important. Is it judged whether the wireless performance of a mobile phone only depends on the strength of the signal? For example, the wifi throughput of 4G mobile phones and 802.11ac in the future is also directly related to antennas, channel correlation, and chip baseband algorithms. The average person habitually calls the wireless performance of the mobile phone as "strong" or "weak". In fact, besides the strength of the signal, the wireless performance of the mobile phone is directly related to its baseband algorithm, especially after entering 4G, the baseband algorithm. The pros and cons will directly determine the "Internet speed" of the mobile phone - at this level, everyone will truly understand how much difference in the baseband algorithm, such as Qualcomm, Intel, MTK, Spreadtrum, and HiSilior, not just 4-core, 8-core or 32-bit, 64-bit or CPU clock speed is so simple and rigorous to evaluate the performance of a communication chip - but today, we only talk about the signal "strong" and "weak" for the time being. In other words, in fact, the quality of mobile phone wireless performance depends partly on the overall RF or antenna design, and the other depends on the baseband algorithm (communication chip), but my discussion today is limited to the RF and antenna levels. One thing to keep in mind is that more and more mobile phones, especially 4G mobile phones, will have a baseband algorithm that will affect the wireless performance of the whole machine and directly reflect the Internet speed. Focusing only on RF design or signal "strong" and "weak" is an outdated, one-sided view. The strength of the mobile phone signal is determined by the mobile phone itself and by the operator's network. The network coverage of operators is mainly related to the layout and transmission power of base stations. There are specialized network optimization departments within each operator to do related optimization work for network load conditions and signal coverage blind areas to ensure the most user experience. Good, of course, if the performance of the mobile phone is better, the requirements for the network are relatively lower. Therefore, when the mobile phone is collected, the operator needs to test the wireless performance of the mobile phone. As a general user, we may be able to choose different operators, but we can't control the network status of the operators, so the average person is more operable, pay attention to the wireless performance of the mobile phone, and then choose a better performance. In this way, under the same network coverage, the Internet speed and call quality can be better than others. For the mobile phone's own RF and antenna design, in fact, we generally focus on the power of the mobile phone to transmit outside (can be understood as the size of the door), and the receiving sensitivity (such as the sound that the ear can hear), in addition to their own design In addition to the pros and cons, it is also related to the electromagnetic compatibility design of the whole machine. Take the receiving sensitivity as an example. If your ear can hear a small sound, but if the noise of the surrounding environment (electromagnetic interference on the board) is too large, you I can't hear what the other party said. This problem is particularly prominent on mobile phones. Because the mobile phone is as big as a palm, the components and various modules and antennas are densely packed, and the board design is slightly inappropriate. Mutual interference occurs between modules, or the signal-to-noise ratio in the receiver system deteriorates due to EMI (Electro-MagneTIc Interference). Suizhou simi intelligent technology development co., LTD , https://www.msmvape.com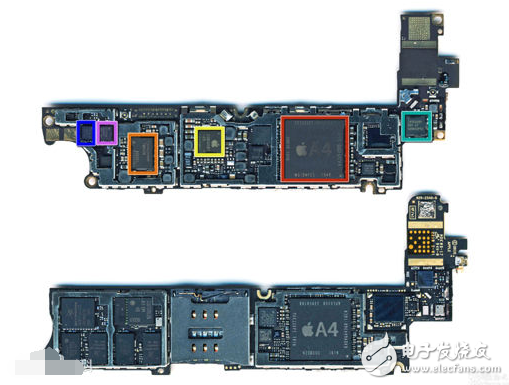

The relationship between the baseband chip and the mobile phone signal
What is a baseband chip?