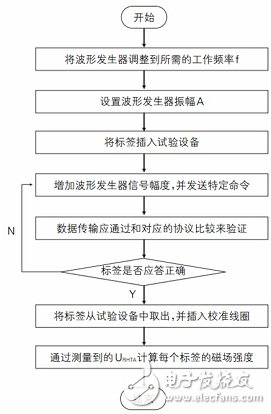
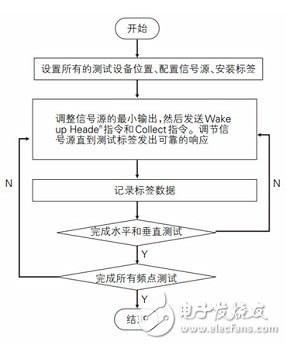
In practical applications, the application of RFID systems should consider the factors affecting system performance, such as location, distance, temperature, humidity, and interference. Untested RFID systems, the overall performance of the system is not clear, may affect the actual application effect, and even combat the end user's confidence in the RFID technology itself. Different wireless signal propagation methods require different test equipment support and different methods are used. ISO/IEC 18047-3 defines test methods for the performance characteristics of RFID tags for item management, specifying general requirements and test requirements for tag performance. The following is an analysis of each specific test content. Functional test of inductive labels conforming to ISO/IEC18000-2, ISO/IEC 18000-3 and ISO/IEC18000-6 This part specifies the test content and test methods of the inductive tag, including the identification of the magnetic field strength threshold, the read magnetic field strength threshold, the write magnetic field strength threshold, the maximum working magnetic field strength, the living magnetic field strength, and the load modulation. For different test contents, the test method is similar: first set the test work frequency, then set the amplitude of the waveform generator, then put the label into the test device, send a specific command, and gradually increase the amplitude until the tag responds. Then, according to different test content, make targeted measurements, record the test results and calculate the value of the test content. Taking the identification of the magnetic field strength threshold as an example, the flow chart 1 shows that URHTA is the amplitude of the current waveform generator. Figure 1 Test procedure for identifying magnetic field strength thresholds for 18000-2 tags The difference in the test process under different protocols is mainly reflected in the various parameter changes and instruction differences in the test process, specifically: Test frequency In the inductive label test, the corresponding frequency in the label test conforming to the ISO/IEC 18000-2 protocol is 125 kHz or 134.2 kHz; the corresponding frequency in the label test conforming to the ISO/IEC 18000-3 protocol is 13.56 MHz; in accordance with ISO/IEC 18000 The corresponding frequencies in the label test of the -6 protocol are one step frequency every 5 MHz from 860 MHz to 960 MHz, and the other three frequencies are 866 MHz, 915 MHz, and 953 MHz. Test initial amplitude In the test for identifying the magnetic field strength threshold, the read magnetic field strength threshold, and the written magnetic field strength threshold, the initial amplitude of the signal generator is set to identify below the magnetic field strength threshold (generally 0); and the maximum working magnetic field strength, survival magnetic field strength, load modulation In the test, the initial amplitude is set to identify the magnetic field strength threshold. Test instruction In the test for identifying the magnetic field strength threshold, the maximum working magnetic field strength, the living magnetic field strength, and the load modulation, the "inventory command" is used; in the test of the read magnetic field strength threshold and the write magnetic field strength threshold, "read command" and "write command" are respectively used. ". In addition, in the maximum working magnetic field strength test, "inquiry command" can also be used. Test result value In the test of the magnetic field strength threshold, the read magnetic field strength threshold, and the write magnetic field strength threshold, the value of the test result is the maximum value of all test record values; the maximum working magnetic field strength, the survival magnetic field strength, the load modulation test, and the test result. The value is the minimum of all test record values. Test process The test flow of different protocols on the same test content is the same, and the test process between different test contents is generally similar, but the specific steps are slightly different, such as: read magnetic field strength threshold and write magnetic field strength threshold test, need to The first memory block starts testing until the end of the last memory block; in the test of the maximum working magnetic field strength and the living magnetic field strength, the maximum working magnetic field strength test needs to send the command first, and then adjust the waveform amplitude value, and the survival magnetic field strength test is First adjust the waveform amplitude value and then send the command. Electromagnetic propagation type tag function test This part specifies the test content and test methods of electromagnetic propagation type tags, including identification of electromagnetic field strength threshold and frequency peak, reading electromagnetic field intensity threshold, writing electromagnetic field strength threshold, sensitivity degradation, maximum working electromagnetic field strength, survival electromagnetic field strength, radar scattering cross section change. Rate, interference suppression, maximum recognition rate of change, maximum write rate of change. For all test contents, the test operating frequency is all frequency points with a step of 5 MHz in the 860 MHz to 960 MHz band, and three frequencies of 866 MHz, 915 MHz, and 953 MHz specified in ISO/IEC 18047-6. For different test contents, the test method is very similar to the test procedure of the aforementioned inductive label. The difference in the test process of different test contents mainly exists in the various parameter changes and instruction differences in the test process, etc., specifically: Test initial amplitude In the test of identifying the electromagnetic field intensity threshold and peak value, the reading electromagnetic field intensity threshold, the writing electromagnetic field intensity threshold, and the sensitivity degradation test, the initial amplitude of the signal generator is set to be below the identification magnetic field strength threshold (generally 0); the maximum working electromagnetic field strength, the survival electromagnetic field strength, In the radar cross-section change rate test, the initial amplitude of the signal generator is set to identify the electromagnetic field intensity threshold; in the continuous wave interference suppression test, the amplitude of the signal generator is set to identify the electromagnetic field intensity threshold, and the initial amplitude of the interference generator is set to identify the electromagnetic field. Below the intensity threshold (generally 0), and in the modulation signal interference suppression test, the amplitude of the signal generator is set to be higher than the identification electromagnetic field intensity threshold by 6 dB, and the initial amplitude of the interference generator is set lower than the identification electromagnetic field strength threshold (generally 0) In the maximum recognition rate of change and the maximum rate of write rate test, the initial amplitude of the signal generator is set to be higher than the identification electromagnetic field intensity threshold by 3 dB (maximum above the identification electromagnetic field intensity threshold by 9 dB). Test instruction Sensitivity degradation, maximum working electromagnetic field strength, survival electromagnetic field strength, radar cross-section change rate, maximum recognition change rate, and maximum write change rate are not specified in the specific test; identify electromagnetic field strength threshold, peak value, read electromagnetic field strength threshold, write electromagnetic field In the intensity threshold test, the inventory command, the read command and the write command are respectively used; in the interference suppression test, the continuous wave interference suppression test and the modulation signal interference suppression test specify a specific command, and the continuous wave interference suppression test also needs to send a continuous wave. Test result value In the identification of electromagnetic field strength threshold, reading electromagnetic field strength threshold, writing electromagnetic field strength threshold, sensitivity degradation test, the value of the test result is the maximum value of all test records; the maximum working electromagnetic field strength, the survival electromagnetic field strength, the radar cross-section change rate In the test of interference suppression, maximum recognition change rate, and maximum write change rate, the value of the test result is the minimum value of all test record values. Test process The test flow between different test contents is generally similar, but the specific steps are slightly different, such as: read electromagnetic field strength threshold and write electromagnetic field strength threshold test, you need to start testing from the first memory block until the end of the last memory block; sensitivity In the degradation test, it is necessary to measure all angles in the horizontal and vertical directions; in the interference suppression test, when the continuous wave interference suppression test is performed, the test is stopped until the label cannot respond to the modulation signal command, and in the modulation signal test, until the label is in the determination range The test is stopped at the level of the 50% expected generator command. Functional test of 433.920MHz electromagnetic propagation type tag conforming to ISO/IEC18000-7 protocol This part specifies the functional test content and test methods of the 433.920MHz electromagnetic propagation type tag conforming to ISO/IEC18000-7, including: identification of electromagnetic field strength threshold and frequency tolerance, reading electromagnetic field intensity threshold and frequency tolerance, writing electromagnetic field strength threshold, Sensitivity directionality, interference suppression, maximum working electromagnetic field strength, and survival electromagnetic field strength. Compared to the aforementioned types of label performance tests, the test setup of the 433.920 MHz electromagnetically propagated label conforming to the ISO/IEC 18000-7 protocol is more complicated: the test equipment should be placed in an anechoic chamber or other completely specific location, which is not subject to The effects of interference sources and transmissions (such as reflection, absorption, or blockage of specific signals). The center frequency used for the test was 433.920 MHz, and FSK modulation at 50 kHz was performed. The waveform and timing were as defined in ISO/IEC 18000-7. The source output must be adjustable from 100dB in 10dB steps with a maximum output of at least 10dBm. The modulation of this signal uses a pattern generator to generate the corresponding correct commands and timing. The FSK receiver and decoder are used in the test to receive, decode and send the tag response to the corresponding monitoring software so that the tag's response can be evaluated. For different test contents, the test process is: first set all test equipment positions, configure signal sources, install labels, send corresponding instructions, adjust the signal source until the test label sends a reliable response, and then target according to different test contents. The measurement and record the test results and calculate the value of the test content. Taking the identification of the electromagnetic field strength threshold test as an example, the flow chart 2 is shown. Figure 2 identifies the electromagnetic field strength test process (Functional test of 433.920MHz electromagnetic propagation type tag conforming to ISO/IEC18000-7 protocol) The difference in testing of different test contents mainly exists in various parameter changes and instruction differences in the test flow, etc., specifically: Test frequency In the test of identifying the electromagnetic field intensity threshold and frequency tolerance, reading the electromagnetic field intensity threshold and frequency tolerance, and writing the electromagnetic field intensity threshold, it is necessary to test 433.900MHz, 433.920MHz, and 433.940MHz; sensitivity directionality, maximum working electromagnetic field strength, and surviving electromagnetic field strength. Only 433.920 MHz needs to be tested in the test; in the interference suppression, the interference frequencies of 433.920 MHz, 434.170 MHz, 433.670 MHz, 434.420 MHz, and 433.420 MHz need to be tested. Test distance In the identification of electromagnetic field intensity threshold and frequency tolerance, read electromagnetic field intensity threshold and frequency tolerance, write electromagnetic field strength threshold, sensitivity directionality, interference suppression test, the recommended test position of the tag position to the reference antenna is 2m, and it is better to use 3m. In the test of the maximum working electromagnetic field strength and the survival electromagnetic field strength, the recommended test position to the reference antenna is 2m, and it is better to use 1m. Test instruction Write the electromagnetic field strength threshold and frequency tolerance test first send Wakeup Header instruction, then send write instruction; in other test items, first send Wakeup Header instruction, then send Collect instruction. Test result value In the identification of electromagnetic field intensity threshold and frequency tolerance, read electromagnetic field intensity threshold and frequency tolerance, write electromagnetic field strength threshold, sensitivity directionality test, the test results take the maximum of all measured values; interference suppression, maximum working electromagnetic field strength, survival In the electromagnetic field strength test, the test result takes the minimum of all measured values. Test process The test process between different test contents is generally similar, but the specific steps are slightly different. For example, in the sensitivity directional test, the label needs to be rotated in 15° steps, and the horizontal direction is 0, 15, 30, 45, 60, respectively. Tested at 75, 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165, 180, 195, 210, 225, 240, 255, 270, 285, 300, 315, 330, and 345 degrees, with vertical directions at 0, 15, respectively. Measurements are made on 30, 45, 60, 75, 90; in the interference suppression test, the signal source strength is set to be higher than ETHR Read 3dB, the interference signal source signal strength is set to be lower than ETHR Read 20dB, and then the interference is adjusted in 3dB steps. Signal source, the channel interference of the test tag suppresses the IRejecTIon value, and repeats the test on the first adjacent channel (250KHz) and the second adjacent channel (500KHz); in the maximum working electromagnetic field strength test, it is necessary to add a signal between the signal source and the antenna. Power amplifier; In the surviving electromagnetic field strength test, the signal generator power needs to be adjusted to be higher than Emax, then return to ETHR IdenTIficaTIon and Emax, and try to read the tag. In practical applications, the application of RFID systems should consider the factors affecting system performance, such as location, distance, temperature, humidity, and interference. Untested RFID systems, the overall performance of the system is not clear, may affect the actual application effect, and even combat the end user's confidence in the RFID technology itself. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct certain tests and simulation tests in accordance with test methods and procedures before investing in and implementing RFID solutions. ISO/IEC 18046-3 is a test method for RFID tag performance, which is conducive to label selection and system design, and is conducive to promoting the better implementation of RFID systems. Temperature And Humidity Sensor The temperature and humidity sensors mostly use the temperature and humidity integrated probe as the temperature measuring element to collect the temperature and humidity signals, which are converted into current signals or voltage signals that have a linear relationship with temperature and humidity after being processed by circuits such as voltage stabilizing filter, operation amplification, nonlinear correction, V / I conversion, constant current and reverse protection, It can also output 485 or 232 interfaces directly through the main control chip. Temperature And Humidity Sensor,Dry Cell Temperature And Humidity Sensor,Humidity And Temperature Sensor,Industrial Humidity And Temperature Sensor Taizhou Jiabo Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jbcbyq.com