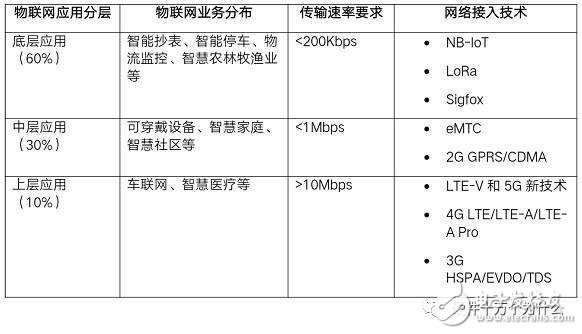
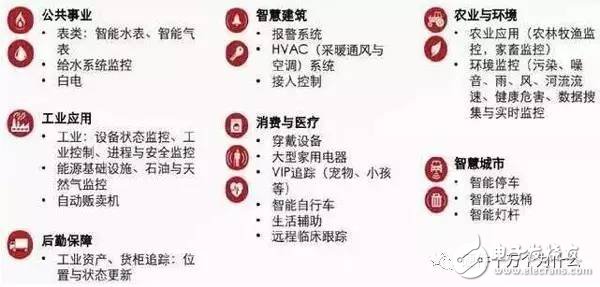
On August 3 and August 4, China Mobile moved tens of billions of dollars and launched two consecutive items to start the IoT project procurement: 1) 39.5 billion yuan to start the 2017-2018 cellular Internet of Things project wireless and core network equipment design and feasibility study collection. The estimated $39.5 billion acquisition includes both NB-IoT and eMTC IoT technology requirements. What exactly is NB-IoT? There are many wireless communication technologies in the Internet of Things, which are mainly divided into two categories: Short-range communication technology: Zigbee, WiFi, Bluetooth, Z-wave, etc.; WAN communication technology: LPWAN (low-power Wide-Area Network) LPWA can be divided into two categories: One is LoRa, SigFox and other technologies that work on unlicensed spectrum; The other is 2/3/4G cellular communication technologies supported by 3GPP, such as EC-GSM, LTE Cat-m, NB-IoT, etc., operating under the licensed spectrum. NB-IoT refers to the Narrow Band - Internet of Things technology. Focusing on the low-power wide coverage (LPWA) Internet of Things (IoT) market, NB-IOT is an emerging technology that can be used globally. The NB-IOT uses the license band and can adopt three deployment modes: in-band, guard band, or independent carrier to coexist with the existing network. NB-IoT is an emerging Internet of Things technology. Because of its low power consumption, stable connection, low cost, and excellent architecture optimization, Huawei has attracted much attention as a leading company in the domestic research and development of NB-IoT technology. NB-IoT has several features: First, wide coverage Will provide improved indoor coverage, in the same frequency band, NB-IoT gains 20dB over the existing network, equivalent to the ability to increase the coverage area by 100 times; The downlink uses OFDMA with subcarrier spacing of 15 kHz. The uplink uses SC-FDMA, Single-tone: 3.75 kHz/15 kHz, Multi-tone: 15 kHz. Only half-duplex support is required, with separate sync signals. The terminal supports instructions for Single-tone and Multi-tone capabilities. The MAC/RLC/PDCP/RRC layer processing is based on existing LTE processes and protocols, and the physical layer performs correlation optimization. NB-IoT has a 20dB gain over LTE and GPRS base stations, and is expected to cover areas where underground signals such as underground garages, basements, and underground pipes are difficult to reach. According to the simulation test data, the NB-IoT coverage capability can reach 164dB in the independent deployment mode, and the in-band deployment and protection band deployment have yet to be simulated. Why is NB-IoT covered? (1) Repeat transmission to extend the transmission time of signal symbols. The repeated transmission of symbols is in fact a simplest channel coding. Although the transmission rate of information is reduced, the reliability in demodulation or decoding is particularly effective in a reception environment with low signal to noise ratio. For example, the ideal decoding error probability is 10%, and the number of repetitions is increased, so that the overall decoding error probability is greatly reduced. (2) Existing TTI bundling and HARQ retransmission techniques can also achieve extended signal symbol transmission time. The associated increased coverage values ​​have proven to be effective in improving signal coverage in VoLTE's commercial networking practices. Second, the ability to support massive connections NB-IoT supports tens of thousands of connections in one sector, supporting low latency sensitivity, ultra-low device cost, low device power consumption and optimized network architecture; NB-IoT has 50 to 100 times higher uplink capacity than 2G/3G/4G. In the same base station, NB-IoT can provide 50~100 times more access than existing wireless technology. Below 200KHz frequency, according to the simulation test data, a single base station cell can support 50,000 NB-IoT terminal access. Third, lower power consumption        What is the target of NB for terminal power consumption? The answer is: based on AA (5000mAh) battery, the service life can exceed 10 years. (An iPhone 7P battery capacity is 2900mAh ). The two main power-saving technologies used in NB are PSM and eDRX. 1, PSM (Power Saving Mode) The technical principle of PSM is very simple, that is, a new state PSM (sub-state of idle) is newly added in the IDLE state. In this state, the terminal radio is turned off, which is equivalent to the shutdown state. This feature was introduced in Release 12 of 3GPP, and the related protocol specifications are in 24.301-5.3.11 Power saving mode and 23.682-4.5.4 UE Power Saving Mode. In the PSM state, the downlink is unreachable. After the DDN arrives at the MME, the MME notifies the SGW to buffer the downlink data of the user and delays the triggering of the paging. When the uplink data/signaling needs to be sent, the terminal is triggered to enter the connected state. When the terminal enters the PSM state, and the duration in which the PSM state resides is negotiated by the core network and the terminal. If the device supports PSM (Power Saving Mode), apply for an activation timer value to the network during the Attach or TAU (Tracking Area Update) process. The timer starts running when the device transitions from the connected state to idle. When the timer expires, the device enters power save mode. (PS: Here are actually two timers, T3324 and T3412 respectively. If you want to listen to it, please go to 601, only for beauty). After entering the power saving mode, the device no longer receives the paging message. It seems that the device and the network are disconnected, but the device is still registered in the network. After the UE enters the PSM mode, the PSM mode is exited only when the UE needs to send MO data or the period TAU/RAU timer expires. The maximum period of the TAU is 310 hours. Here, some data from the chip manufacturer are used to illustrate the power saving effect in the PSM mode. From this, it can be seen that the power consumption in the PSM mode and the power consumption in the normal idle state are 1/200, and the power saving effect is over. The advantage of PSM is that it can be used for long-term sleep. The disadvantage is that the MT (called) service response is not timely, and it is mainly applied to services such as table types that do not require low real-time downlink. In fact, the communication requirements of IoT devices are different from those of mobile phones, and it is for this reason that PSM mode can be designed. The Internet of Things usually only sends packets upstream, and whether or not the packets are sent is determined by itself. It does not need to wait for calls from other terminals at any time, and the mobile phone is not waiting for the call request initiated by the network. If you design the communication of the Internet of Things in the way of 2G/3G/4G, it means that the device of the Internet of Things behaves like a mobile phone, which wastes a lot of power consumption on the request that the monitoring network may initiate at any time. Consumption. Based on the NB-IoT technology, the IoT terminal immediately enters a dormant state after sending a data packet, and no longer performs any communication activities. When it has a request for reporting data, it wakes up itself, then sends the data, and then sends the data. Going to sleep again. According to the behavior of the IoT terminal, it will reach 99% of the time in the sleep state, so the power consumption will be very low. 2. eDRX (Extended DRX) As a new feature in Rel-13, eDRX is mainly designed to support longer-cycle paging monitoring to achieve power saving. The traditional 2.56s paging interval consumes a lot of power for the IOT terminal. When the downlink data transmission frequency is small, the terminal skips most of the paging monitoring through the negotiation of the core network and the terminal, thereby achieving the purpose of power saving. . The terminal and core network negotiate the length of eDRX through the attach and TAU processes.         It can be seen that eDRX consumes 1/16 of DRX, and the power saving effect is also very impressive. Although the power saving effect is worse than that of the PSM, the reachability of the downlink communication link is greatly improved relative to the PSM. At present, the cost advantage of NB has not been seen, and the price is still relatively high. At present, the price of a single module has already been around 80¥. Due to the common promotion of the whole industry, there should be room for further price reduction. However, the price of the GPRS module with a distance of 20 ¥ is still quite different. Manufacturers are waiting for the industry to start, users are waiting for manufacturers to cut prices. In short, everyone is waiting for NB-IoT's Moore's Law . Focusing on the Low Power Wide Coverage (LPWA) Internet of Things (IoT) market, NB-IOT is an emerging technology that can be used globally. It has the characteristics of wide coverage, many connections, low speed, low cost, low power consumption and excellent architecture. The NB-IOT uses the license band and can be deployed in the inband, guard band or independent carrier mode to coexist with the existing network. Because NB-IoT has its own advantages of low power consumption, wide coverage, large capacity, etc., after its price sinks, it can be widely used in a variety of vertical industries, such as remote meter reading, asset tracking, intelligent parking, smart agriculture, etc. . The first version of the 3GPP standard is expected to be released in June this year, when a number of test networks and small-scale commercial networks will emerge. The three major operators of domestic mobile, telecommunications and China Unicom have also begun to take action. Telecom first established an experimental network in Nanjing last November. This year, it has officially commercialized the first NB-IoT network in Yingtan. At the same time, Telecom also released the NB-IoT Enterprise Standard V1.0. Mobile also built a smart streetlight project in Nanjing through NB-IoT technology. As early as June 2016, China Unicom deployed 10 outdoor sites based on NB-IoT in Shanghai Disneyland to cover the entire campus. In October, China Unicom opened the first standardized NB-IoT commercial network in Guangzhou. The three major operators have increased their focus and investment in the NB-IoT field to find new business growth points. Intelligent meter reading system Shared bike selection NB-IoT Whether it is the cooperation between Mobai and Ericsson and China Mobile, or the cooperation between ofo and Huawei and China Telecom, the key words are “NB-IoT†(NB-IoT). NB-IoT is designed to solve the problem of low-power, low-bandwidth, long-distance transmission network connections between a large number of objects, and belongs to the LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) category. Before the birth of NB-IoT, LoRa was more familiar in the field. LoRa is a private low-speed Internet of Things technology proposed by Semtech of the United States. Semtech also initiated the formation of the LoRa Alliance. The alliance was established in March 2015 and has already joined more than 400 companies including IBM, Cisco and Microchip. The alliance. Many companies have a certain division of labor in the alliance, including system solution providers, software vendors, chip vendors, module vendors, terminal equipment vendors and a small number of operators. NB-IoT is an open technology standard promoted by the 3GPP organization. Based on mature cellular technology, it adds frequency hopping and anti-jamming technology, and more advanced wireless resource utilization technology to adapt to the regulations and propagation environment of unlicensed spectrum. Its alliance members also include Huawei, Intel, Qualcomm, Ericsson and other companies and operators including China Mobile, Telecom, China Unicom, Vodafone, Deutsche Telekom, Telefónica and other operators. In the LPWA field, LoRa has a significant competitive relationship with NB-IoT. And with the commercialization of solutions based on the NB-IoT standard in the market, the competition in the face of huge potential market is the beginning. As a latecomer, NB-IoT has some "innate" advantages. Three advantages or will determine the development limit First, there is a big difference between the development and evolution of technical standards. As mentioned above, LoRa technology was proposed by Semtech, which plays an important role in the alliance as a chip supplier, including Chirp modulation, synchronization, error correction, frame structure, networking, and chip architecture. The technical details are protected by corresponding patents, and more companies are licensed to create LoRa chips using ARM-like chip licensing. This situation is unwilling to be seen by a large number of potential customers, especially in emerging markets such as LPWA. In contrast, NB-IoT, such as Huawei, Intel, Qualcomm and other companies have the corresponding chip design capabilities, and has released several NB-IoT chips. This makes there is enough internal competition and screening in the field of NB-IoT, so that we can learn from others in the development process. Second, the key performance NB-IoT dominates. From the perspective of existing products, NB-IoT products based on carrier cellular networks have better performance in link transmission performance and security. Especially under high load conditions, the performance advantages will be more obvious. For different industry applications, NB-IoT, which has many chip designers, is more likely to meet complex industry needs after the business model is launched. Third, the advantages in the ecological chain. The LoRa Alliance uses a chip-licensed approach to build a complete solution for different vendors. There are some uncertainties in this seemingly flexible solution. Just as in the traditional ICT market, how can it be quickly located once such an integration solution fails? This undoubtedly increases the cost and maintenance costs. The difficulty is also due to the rapid deployment and maintenance of the industry private network. NB-IoT has attracted more large telecom operators and mainstream industry solution providers. Many of these experienced vendors can provide end-to-end industry solutions. It is reported that NB-IoT solution vendors can provide unified delivery on the network side to avoid problems such as network-side interconnection testing and multi-party maintenance brought by different manufacturers. Regarding the current problem of NB, at the end of an article in the previous two days, the opinion expressed by a hard friend "I don't call Wang Da hammer" is not unreasonable: What are the original NB-IoT chips and their models? NB-IoT chip vendors are mainly from GSM/LTE Modem, and there are also MCU companies like WiFi/BT. In the future, more NB-IoT chip manufacturers will intervene and expect to enter price competition in 2017. The original NB-IoT chip is as follows: 1. Qualcomm Headquarters: United States Main: Snapdragon mobile processor platform, wireless chipset, 3G/4G chipset, system software and development tools and products, wireless solutions. Main NB-IoT chip model : MDM9206 Time : Mass production at the end of May Features : Supports all frequency bands of Cat-M1 and Cat-NB1 LTE worldwide, eMTC/NB-IoT/GSM multi-mode support, integrated GPS, Gennaros, Beidou and Galileo global navigation satellite positioning. service. Official website: http:// 2, Huawei Haisi Headquarters: Shenzhen Main: network monitoring chip, video phone chip, DVB chip, IPTV chip. Main NB-IoT chip model: Boudica 120/Hi2110 Time: Mass production at the end of June Product features: equipped with Huawei LiteOS embedded IoT operating system SOC: BB+RF+PMU+AP+Memory; 3 ARM Core: AP+CP+SP" Main NB-IoT chip model: Boudica 150 Time: Q4 mass production Product features: can support 698-960/1800/2100MHz Official website: http:// 3. Rydike (RDA) Headquarters: Shanghai Main: GSM baseband / multi-standard RF transceiver chip / multi-standard RF power amplifier chip / Bluetooth, wireless, FM radio chip / set-top box tuner / digital and analog TV chip / walkie-talkie transceiver / satellite TV tuner. Main NB-IoT chip model: RDA8909 Time: Mass production at the end of June Features: Support 2G, NB-IoT dual mode, RDA8909 conforms to 3GPP R13 NB-IoT standard, and can also support the latest 3GPP R14 standard through software upgrade Main NB-IoT chip model: RDA8910 Time: 2018YQ2 mass production Product features: support eMTC, NB-IoT and GPRS three-mode Official website: http:// 4. ZTE Microelectronics Headquarters: Shenzhen Main NB-IoT chip model: Wisefone 7100 Time: Commercial at the end of September Features: Full-featured full-band NB-IoT chip with integrated CK802 chip from Zhongtian Microsystem Official website: http:// 5, Intel (Intel) Headquarters: United States Main: integrated chip design, motherboard chipset, network card, flash memory, graphics chip, embedded processor. Main NB-IoT chip model: XMM 7115 Time: No samples yet Product features: support NB-IoT standard Main NB-IoT chip model: XMM 7315 Time: Q4 mass production Features: Supports LTE Category M and NB-IoT standards, single chip integrated LTE modem and IA application processor Official website: http:// 6, Altair (acquired by Sony) Headquarters: Israel Main: Altair is a chip design (IC) company that produces 4G technology terminal baseband processors. It also designs 4G terminal chip RF transceivers for FDD and TDD bands. Main NB-IoT chip model: ALT1250 Time: Mass production at the end of July Features: Cat-M and Cat-NB1, integrated GPS, 90% of components in cellular IoT modules - such as RF, baseband, front-end components, power amplifiers, filters and switches - have been integrated into the ALT1250 7, Sequans (Sequans) Main NB-IoT chip model: Monarch SX Time: Mass production at the end of July Features: Based on Sequans' Monarch LTE-M / NB-IoT platform with baseband, RF, RAM and power management, and integrated: ARM Cortex-M4 processor Media processing engine for audio and voice applications, including support for VoLTE over LTE-M Low power sensor hub GPU and display controller IoT interface for USB, screen, microphone, battery, GNSS, SIM card, secure element, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth low energy, keyboard, accelerometer, gyroscope and other sensors Single chip FC-CSP package 8, Nordic Headquarters: Norway Main: Nordic Semiconductor is a fabless semiconductor company specializing in ultra-low power (ULP) short-range wireless communications in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz band and industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) bands below 1 GHz. technology. Customers can take advantage of Nordic's Ultra Low Power (ULP) wireless solutions to add wireless connectivity to a wide range of products. Main NB-IoT chip model: nRF91 Time: Samples will be available in the second half of 2017 and will be available in 2018 Features: 3GPP Release 13 LTE-M and NB-IoT Official website: http:// 9, GCT Main: GCT Semiconductor is a leading fabless semiconductor company providing innovative IC solutions for the wireless communications industry. Main NB-IoT chip model: GDM7243I Time: Q3 mass production Features: LTE Category MI/NB1, highly integrated with RF transceiver, baseband and RAM memory Cat-M1 (1.4MHz) Cat-NB1 (200KHz) Official website: http:// 10. MediaTek (MTK) Headquarters: Taiwan Main: wireless communication and digital multimedia chip integration system solutions Main NB-IoT chip model: unknown Time: Q4 mass production Official website: http:// 11, simple nano Headquarters: Suzhou Main: mainly engaged in the development of baseband processor architecture and CPU/DSP core for next-generation mobile communication, development of supporting multi-mode communication protocol stack and development tools, and low-power, low-cost, programmable, multimedia terminal baseband SoC chip. The current product directions are: - GSM/GPRS/EDGE+GPS terminal processing chip and terminal solution for 2G/2.5G wireless communication network - TD-LTE wireless terminal processing chip and terminal module solution for 3.9G wireless communication network - Near Field Communication (NFC) based on 2.4G/5.8GHz frequency. Main NB-IoT chip model: unknown Official website: http:// 12. MARVELL Headquarters: United States Main: microprocessor architecture and digital signal processing. Main NB-IoT chip model: unknown Official website: http:// What are the NB-IoT module manufacturers? The application of NB-IoT is too extensive, and the concentration of NB-IoT module manufacturers is not as high as that of chip manufacturers. The NB-IoT module manufacturers are as follows: 1. Shanghai Mobile Communication Technology Co., Ltd. (Quectel) Headquarters: Shanghai Main: Quectel Wireless Solutions is the world's leading provider of GSM / GPRS, UMTS / HSPA / (+), LTE and GNSS modules. Main NB-IoT module model: BC95-B20/B8/B5/B28 NB-IoT chip used: Huawei Hais Boudica Quectel is based on the BC95 module of the Boudica 120 Main NB-IoT module model: BG96 module NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm MDM9206 Quectel BG96 module based on MDM9206 Official website: http:// 2. Shenzhen Zhongxing IOT Technology Co., Ltd. Headquarters: Shenzhen Main: Committed to more, smarter, safer and more reliable wireless connections and services, covering a wide range of standard and packaged communication module products, vehicle networking communication terminal products, industry special terminals and IoT total solutions, and Continuous innovation and excellent quality have been recognized by various industries at home and abroad. Main NB-IoT module model: ME3612 NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm MDM9206 Official website: http:// 3, Ublox Headquarters: United States Main NB-IoT module model: SARA-N201 NB-IoT chip used: Huawei Hais Boudica Official website: http:// 4, Lierda Technology Co., Ltd. Headquarters: Shenzhen Main NB-IoT module model: NB05-01 NB-IoT chip used: Huawei Hais Boudica Official website: http:// 5, Shenzhen Youfang Technology Co., Ltd. Headquarters: Shenzhen Main: Focus on the mining and implementation of wireless application requirements, provide professional LTE, WCDMA, EVDO, GPRS, CDMA 1X, short-range wireless and other communication system industrial module products and industrial IoT solutions, with product planning, industrial design, structure, hardware, software, testing, ID, logistics, R & D and design a complete system, the core R & D team are from the domestic industry's leading wireless communications companies. Main NB-IoT module model: N20 NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm MDM9206 Official website: http:// 6. Shanghai Shike Communication Technology Co., Ltd. Headquarters: Shanghai Main: It is an industry leading GSM/GPRS, WCDMA/LTE, NB-IoT, GPS/GNSS module supplier. The company is committed to providing intelligent and non-intelligent wireless module products and applications. Main NB-IoT module model: L700 NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm MDM9206 Official website: http:// 7. Core Communication Wireless Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Main: The world's leading M2M module and solution provider. Has committed to provide the terminal or module-level GSM / GPRS / EDGE, WCDMA / HSPA / HSPA +, CDMA 1xRTT / EV-DO, FDD / TDD-LTE wireless cellular communications and GPS / GLONASS / BEIDOU other satellite positioning technology platforms solution. Main NB-IoT module model: SIM7000C NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm MDM9206 Official website: http:// 8. Longshang Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Main: The world's leading provider of information and communication solutions. It provides solutions for GSM/GPRS/EDGE, WCDMA, CDMA1X/EVDO, TD-SCDMA and LTE full range of wireless communication modules and IoT applications based on wireless communication modules. Main NB-IoT module model: A9500 NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm MDM9206 Official website: http:// 9. China Mobile Internet of Things Co., Ltd. Headquarters: Chongqing Main: A wholly-owned subsidiary funded by China Mobile Communications Corporation. The supporter of IoT business services, the provider of dedicated modules and chips, and the promoters of IoT-specific products. Main NB-IoT module model: M5310 NB-IoT chip used: Huawei HiShip Hi2110 Official website: http://iot.10086.cn/ 10, Lenovo understands the communication Main: Leading intelligent IoT service provider. Main NB-IoT module model: C1100 NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm MDM9206 11. Shenzhen Guanghetong Wireless Co., Ltd. Headquarters: Shenzhen Main: The first wireless communication module and solution provider in China (stock code: 300638). Fibocom brand products cover LTE, NB-IoT/eMTC, HSPA+, GSM/GPRS wireless communication modules and solutions. The major shareholders include Intel, the world 's largest personal computer parts and CPU manufacturer. Main NB-IoT module model: Fibocom N50 NB-IoT chip used: Intel XMM7115 FIBOCOM based on XMM7115 module N510 Main NB-IoT module model: unknown NB-IoT chip used: RDA Official website: http:// 12, Telit Headquarters: London, UK Main: Telit is the global leader in the implementation of the Internet of Things (IoT). Main NB-IoT module model: unknown NB-IoT chip used: Intel Official website: http:// 13. Shenzhen Meige Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. Headquarters: Shenzhen Main: The company's core business is the development and production of IoT intelligent terminals, wireless communication modules (M2M) and intelligent hardware based on next-generation information technology and long-distance wireless data transmission technology, as well as precision mold development and precision component production. Sales. The company's IoT intelligent terminal, LTE module products and wireless data solutions have formed large-scale in the fields of security monitoring, mobile payment finance POS, vehicle (machine) intelligent rearview mirror, DTU, charging pile, police service, logistics and handheld. application. Precision Components business has entered the ranks of China's top supplier of core consumer brands. Main NB-IoT module model: SLM150 NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm Official website: http:// 14. Xiamen Yujun IOT Technology Co., Ltd. Headquarters: Xiamen Main: IoT integrated solution provider focusing on location service and wireless communication technology, GNSS/GPRS positioning terminal designed and developed by the company for customer needs, GSM/GPRS series, WCDMA series, LTE series wireless communication terminal, etc. of products and related software technology can be widely used in smart home, smart transportation, smart utilities, mobile payments and other things segments. Main NB-IoT module model: ML3500 NB-IoT chip used: Qualcomm Official website: http:// 15, Sierra Wireless Headquarters: Canada Main: Provide hardware, software and services in the wireless market to provide customers with innovative, reliable and high-performance solutions. Main NB-IoT module model: unknown NB-IoT chip used: Altair Official website: https:// 16, Gemalto Main NB-IoT module model: unknown NB-IoT chip used: Sequans Top 10 questions and answers about NB-IoT Q1: Does the NB-IoT module also require a sim card? A: It should be noted that the current development of NB-IoT chips still requires carrier network support and requires a SIM card. In other words, the NB-IoT module requires a network access license as specified by each country. The SIM card and IMEI number need to be bound. Q2: How are the frequency bands of NB-IoT allocated by domestic and foreign operators? A: Most operators around the world use the 900MHz band to deploy NB-IoT, and some carriers are deployed in the 800MHz band. China Unicom's NB-IoT is deployed in the 900MHz and 1800MHz bands, and currently only 900MHz can be tested. In order to build the NB-IoT Internet of Things, China Mobile will obtain an FDD license and allow the existing 900MHz and 1800MHz bands to be re-cultivated. China Telecom's NB-IoT is deployed in the 800MHz band with a frequency of only 5MHz. Q3: What is the available NB-IoT band owned by domestic operators? A: In 2016, China Unicom launched a 900MHz, 1800MHz NB-IoT field-scale networking test in seven cities (Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Fuzhou, Changsha, Yinchuan) and more than six business application demonstrations. In 2018, the nationwide NB-IoT commercial deployment will be fully promoted. China Mobile plans to start the commercialization of NB-IoT in 2017. China Telecom plans to deploy the NB-IoT network in the first half of 2017. Huawei has established six NB-IoT open labs in conjunction with six operators (China Unicom, China Mobile, Vodafone, Emirates Telecom, Telefonica, Telecom Italia) to focus on NB-IoT business innovation, industry development, and interoperability testing. Verification with product compatibility. ZTE and China Mobile completed the technical verification demonstration of the NB-IoT protocol at the China Mobile 5G Joint Innovation Center Laboratory. Q4: Will the NB-IoT standard support TDD LTE? A: At present, the FDD LTE system supports NB-IoT technology. Currently, the TDD LTE system does not support NB-IoT technology. Most of the physical layer design of NB-IoT follows the LTE system technology, such as SC-FDMA for uplink and OFDM for downlink. The high-level protocol design follows the LTE protocol and is enhanced for its small data packets, low power consumption, and large connectivity features. The core network is based on the S1 interface and supports independent deployment and upgrade deployment. Q5: Does NB-IoT support base station positioning? A: R13 does not support base station positioning, but the carrier network can be used as a private solution. For example, cell ID-based positioning does not affect the terminal. Only the network needs to add a positioning server and contact with the base station. The R14 plans to do positioning enhancements to support E-CID, UTDOA or OTDOA. The operator's desired positioning accuracy target is within 50 meters. UTDOA is better if it is considered from the perspective of terminal complexity, because there is almost no impact on the terminal, and in the case of coverage enhancement (164dB in the basement), UTDOA (uplink) power consumption is lower; if most scenarios do not require coverage enhancement, the slave network From a capacity perspective, OTDOA (downstream) will be better. Q6: What modulation and demodulation technology does NB-IoT use? A: The downlink uses OFDMA, and the subcarrier spacing is 15 kHz. The uplink uses SC-FDMA, Single-tone: 3.75 kHz/15 kHz, Multi-tone: 15 kHz. Only half-duplex support is required, with separate sync signals. The terminal supports instructions for Single-tone and Multi-tone capabilities. The MAC/RLC/PDCP/RRC layer processing is based on existing LTE processes and protocols, and the physical layer performs correlation optimization. Q7: What is the number of connected users and the number of active users of the NB-IoT base station? A: NB-IoT has 50~100 times higher uplink capacity than 2G/3G/4G. In the same base station, NB-IoT can provide 50~100 times more access than existing wireless technology. Below 200KHz frequency, according to the simulation test data, a single base station cell can support 50,000 NB-IoT terminal access. Q8: What is the coverage of the NB-IoT base station? A: NB-IoT has a 20dB gain over LTE and GPRS base stations, and it is expected to cover areas where underground signals such as underground garages, basements, and underground pipes are difficult to reach. According to the simulation test data, the NB-IoT coverage capability can reach 164dB in the independent deployment mode, and the in-band deployment and protection band deployment have yet to be simulated. Q9: What is the uplink and downlink transmission rate of NB-IoT? A: The NB-IoT RF bandwidth is 200kHz. Downstream rate: greater than 160kbps, less than 250kbps. Uplink rate: greater than 160 kbps, less than 250 kbps (Multi-tone) / 200 kbps (Single-tone). Q10: Does NB-IoT support voice? A: NB-IoT supports Push to Talk without coverage enhancement. In the 20dB coverage enhanced scene, only support similar to Voice Mail. NB-IoT does not support VoLTE, which requires too much latency, and high-layer protocol stacks require QoS guarantees, which increases costs. NB-IoT technology application scenario: 1. Public utilities: smart water meters, smart water, smart gas meters, smart heat meters. 2. Smart City: Smart parking, smart street lights, smart trash cans, smart manhole covers. 3. Consumer Electronics: Independent wearable devices, smart bicycles, chronic disease management systems, and elderly children management. 4. Equipment management: equipment status monitoring, white goods management, large public infrastructure, pipeline management safety monitoring. 5. Intelligent building: environmental alarm system, central air conditioning supervision, elevator Internet of Things, civil air defense coverage. 6. Command logistics: cold chain logistics, container tracking, fixed asset tracking, financial asset tracking. 7. Agriculture and Environment: Agricultural Internet of Things, animal husbandry, real-time monitoring of air, real-time monitoring of water quality. 8. Other applications: mobile payment, smart community, smart home, cultural relics protection. In terms of finishing, NB-IoT applications are divided into four areas: public service, personal, industrial, new and new business. Among the public service sectors , water, electricity, gas meter smart metering, public parking management, environmental monitoring, etc. are listed as entry points. In the field of personal life , smart home, wearable devices, children and elderly care, pet tracking and consumer electronics, smart home I do not think it is the main application of NB-IoT, but children care and pets It is very promising when tracking. There is also the potential for business model innovation. In the field of industrial manufacturing , "monitoring and control of manufacturing processes", "applications in logistics and transportation, agricultural production, etc.", the application scenario of NB-IoT has great imagination, but it must break through the current industrial field control communication. Technology still has a long way to go. This is a blue ocean market, but in the short term, it may be difficult to see successful scale applications, unless China Mobile or Huawei acquires a manufacturing company to do the whole process demonstration. Freeness can only float on the surface outside the industry. However, in the agricultural field, NB-IoT has a broad space for development. The distribution of agriculture itself is high in many links and the degree of informatization is not high. Therefore, there is a great imagination in product and business model innovation. Part of the content is compiled from "itbank", "Old Wusong Communication", "Mobile Tendering Official Website" and "Net You Mercenary". Precision machining is a kind of machining, which is a workpiece to meet the requirements of the drawing of the line tolerance of the processing process, the workpiece in this process, will have certain changes in their performance characteristics and shape structure. Precision Machining,Casting Exhaust Manifold,Stainless Stee Milling,Custom Cnc Machining Part Tianhui Machine Co.,Ltd , https://www.thcastings.com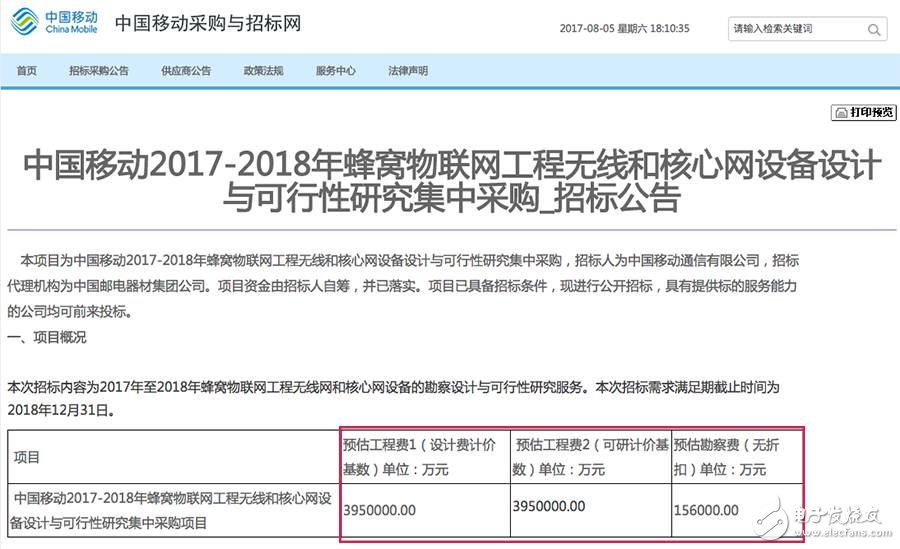

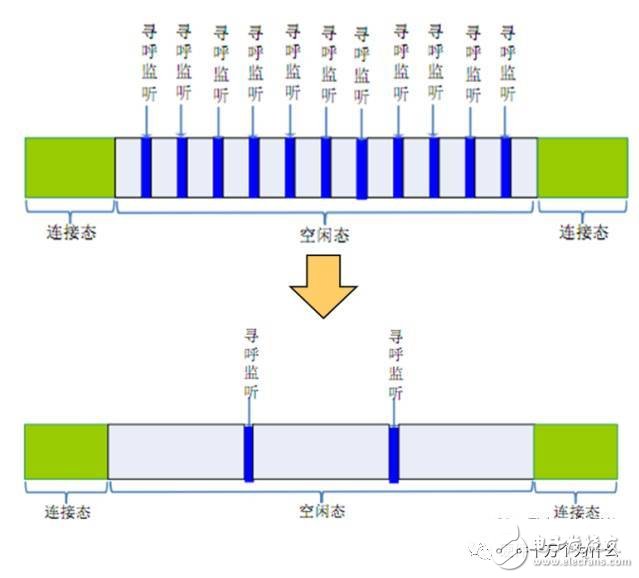
(3) In view of the low rate of NB-IoT service demand, most services can be realized at around 100 bps, so low-order modulation techniques such as BPSK, QPSK, and shorter length CRC check codes can be used.
(4) In terms of coding, NB-IoT adopts Turbo coding, and GPRS adopts convolutional code. The advantage is that the requirement of decoding SNR is reduced, and the corresponding coverage distance is enhanced by 3~4 dB.
(5) The reduction of delay requirements and the use of Power Boost on some downlink physical channels have direct enhancements to signal coverage. 















There are mechanical processing, naturally there are corresponding parts, mechanical parts design as a mechanical major of a subject, is one of the popular majors of science students, is also one of the strongest engineering; At present, this major requires not only good knowledge of science and engineering, but also excellent drawing ability and spatial imagination ability. In addition, due to the development of domestic industry and the constant change of demand, the demand for personnel in the mechanical processing industry is also increasing, and the employment rate of mechanical majors can reach 95%.