Frequency dividing circuit The figure shows a typical crossover circuit diagram--frequency divider circuit one. The frequency dividing circuit plays an extremely important role in the high quality reduction of the electroacoustic signal in the speaker system. Especially in the middle and high frequency parts, the role played by the frequency dividing circuit is more obvious. The function of the frequency division circuit: 1. Reasonably divide the working frequency band of each unit; 2. Reasonably perform power distribution of each unit; 3. Make appropriate phase relationship between units to reduce acoustic interference of each unit during operation. Distortion; 4, the use of the characteristics of the frequency divider circuit to compensate for the sound defects of the unit in a certain frequency band; 5, the smooth and smooth connection of each frequency band. Frequency dividing circuit 2 The figure shows a typical crossover circuit diagram--frequency divider circuit 2. The crossover point refers to the demarcation point between the divider high pass, band pass and low pass filter, expressed in common frequency, in Hertz. The crossover point should be determined based on the frequency characteristics and power distribution of the speaker units or speakers in each band. How to choose the crossover point? 1. Consider the medium-low cell directivity practical boundary frequency f=345/d (d=unit diaphragm effective diameter). Usually, the boundary frequency of the 8" unit is 2k, the boundary frequency of the 6. 5" unit is 2. 7k, the unit of 5" is 3. 4k, and the unit of 4" is 4. 3k. That is to say, using the above unit, the frequency division point cannot be greater than the practical boundary frequency corresponding to each unit. 2. Considering the resonant frequency of the tweeter, the crossover point should be greater than three times the resonant frequency. That is to say, from the perspective of the tweeter, usually the crossover point should be greater than 2. 5k. 3. Consider the high-end response Fh of the mid-woofer unit. Usually, the crossover point should not be greater than 1/2Fh. In fact, the above conditions of the two-way speaker are difficult to obtain at the same time. At this time, the designer should have a better compromise among the three. However, it must be emphasized that the first condition, the practical boundary frequency, should be given priority. 4. In the case of three-way, the farther the two crossover points should be separated (should be above three octaves), the better the system response will be. Otherwise, complex interference radiation will occur. 5, the crossover point of the bass and midrange should consider the problem of vocal image positioning. The playback of the vocals should be undertaken by the midrange unit as much as possible to avoid excessive changes in the vocal positioning sound of the vocals. This is often overlooked by designers. Usually this crossover point should be 200-300Hz. Frequency dividing circuit three The figure shows a typical crossover circuit diagram--divided circuit three. The frequency of sound that humans can hear is between 20 Hz and 20 kHz. Therefore, under normal circumstances, in order to ensure the frequency response and the frequency bandwidth of the reproduced sound, the high-quality split speaker is mostly used in the professional field. When a high-bass split-type speaker is used to deliver sound, it is necessary to separate the sound by frequency band, and the number of sounds divided by frequency is the sound frequency division number. The crossover of the sound is mainly controlled by the speaker, because most speakers have their own most suitable frequency range, and true high quality full range speakers are very rare and extremely expensive. At the same time, in order to overcome the cutting distortion caused by different frequency sound speakers and reduce the sound interference between different speakers in the same speaker, the sound must be divided to send sounds of different frequency bands to different speakers. Frequency dividing circuit four The figure shows a typical crossover circuit diagram--divided circuit four. Advantages of the frequency division circuit: The electronic frequency division (or active, active frequency division) network has the following advantages: 1. The transient response is improved; 2. The operating frequency band of each amplifier is narrowed; 3. The probability of low frequency overload is reduced; 4. The dynamic range is improved; 5. The intermodulation distortion is small; 6. The sensitivity of each unit is easy to control.
E-cig as a substitute of tobacco mainly reminds people of its potential benefits for health. Four ingredients contain in the e-liquid : propylene glycol, glycerin vegetable, nicotine and food grade essence. Nevertheless, smoke from cigarette contains carbon monoxide, tar, arsenic, ammonia, and many other cyanide and acetone.
Advantage
Wax Device Oem,Thc Wax Device Oem,Marijuana Wax Device Oem,High Cost Performance Wax Device Shenzhen MASON VAP Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.cbdvapefactory.com
What are the crossover methods of the crossover circuit? One is PassiveCrossover, or electronic crossover. It can also be called external crossover and active crossover. The other is passive crossover (ActiveCrossover), or power crossover. It can also be called built-in. Frequency division, passive frequency division. Active crossover means that the crossover is not inside the speaker. Before the power is amplified, because the sound signal is very weak at this time, it is easy to divide the sound completely. The disadvantage is that the corresponding electronic circuit crossover point is fixed, not easy and different. Speakers are common in high-end and professional audio. With the popularity of multi-channel amplifiers, active frequency division is much more popular than before. Passive crossover means that the crossover is in the speaker. At this time, the sound signal has been amplified, and the frequency dividing circuit will cause some interference, but the speaker can be applied to different power amplifiers.
The simplest crossover is the divide-by-2, which divides the sound into high-frequency and low-frequency. The crossover point needs to be higher than 1/2 of the upper limit of the woofer, which is lower than twice the lower limit of the tweeter. The general crossover point is Between 2K and 5K. The three-way division divides the sound into bass, midrange and treble. There are two crossover points. The bass crossover point is generally below 200 Hz, or 120 Hz, or even lower. The treble crossover point is generally 2 Hz-6 kHz. There are also a small number of divide-by-way or multi-way systems. Obviously, more frequency divisions are theoretically more conducive to the restoration of sound, but too many crossover points will cause the overall cost to rise, and the actual effect is limited, so the common frequency division is still divided by two and three. 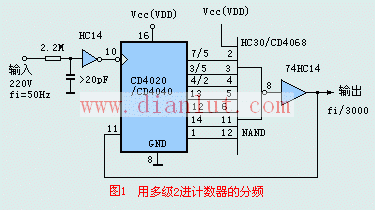
Frequency division circuit and selection of frequency division circuit
1. Improvement of transient response First of all, we must understand the working principle of the speaker (actually not complicated, ordinary high school students should also understand), the most basic theoretical basis of the speaker is the principle of electromagnetic induction. The energized solenoid of the speaker generates a magnetic field that repels or attracts the magnetic field of the speaker to cause vibration of the diaphragm. When an electrical signal completes its mission disappears, the diaphragm still has inertia. By inertial motion, the conductor cutting magnetic induction line also produces an induced electromotive force, and the magnetic field generated by the induced current will produce a motion. The opposite torque pulls the speaker diaphragm back to its original position.
The above is the most ideal, simplest and most basic form of the speaker to complete a signal cycle motion. (In the most ideal state, it is hoped that the speaker diaphragm can be completely electromagnetically controlled, and a current diaphragm should be given to the specified position. It doesn't generate extra vibration.) Although the movement of the speaker is far from simple, it is the basis for people to analyze the problem (even the simplest signal, the impact on the speaker will produce two or three times. The electromotive force, the principle is similar to that mentioned above).
Here, the induced electromotive force is the key point of the electronic crossover technology, because the generated induced electromotive force is related to the final speed after the speaker is accelerated. After generating the induced electromotive force, how much current can be generated needs to see the circuit between the amplifier and the speaker. The impedance is determined, and this will be a key factor in generating the magnitude of the torque. In systems with low impedance, the current will be relatively large and the induced torque will be larger. The faster the speaker returns to its original position. At this point, one can draw a clear conclusion: the smaller the impedance between the amplifier and the speaker, the better. In other words, the smaller the loop impedance of the amplifier to the speaker (high damping coefficient, high braking performance), the stronger the control force on the speaker, the sound will be clean, the transient reflection, and the speed will be heard. The characteristics of this are the first.
2. The operating frequency band of each amplifier is narrowed. Because of the circuit design of frequency-divided and re-amplified, the frequency band of the audio signal received by each group of amplifiers is narrower than that of the conventional power-dividing circuit amplifier.
3. The possibility of low-frequency overload reduction The possibility of low-frequency overload reduction is actually related to the above advantages. It can be said that the possibility of low-frequency overload is one of the results or benefits of narrowing the operating frequency of a single amplifier. Since the middle and low frequencies of the audio signal occupy most of the entire signal energy, the conventional amplifier (assuming the same power amplifier IC is used), when playing back a signal with a large level, if full-frequency amplification is first, it is likely to appear. Sharpening distortion. If you first divide the frequency and then zoom in, it is possible to avoid this. First of all, the high-frequency signal can be separately amplified without being affected by the low-frequency; secondly, after the high-frequency signal is cut off, the amplification bandwidth requirement is reduced, the amplifier IC is amplified, and the redundancy is more abundant, which improves the playback quality. It is good.
In addition to the first-order frequency division and the second-order frequency division, the passive frequency divider has three-order, fourth-order or sixth-order frequency division. The advantage of using high-order crossover is that the filter attenuation slope is larger, the crossover effect is better, and it is also beneficial to design the crossover compensation circuit (because the frequency divider that is not completely "cleaner" is a good crossover. In theory, the two signal curves after frequency division are completely consistent with the original curve after superposition, which is a true good frequency divider), but the power loss of high-order frequency division is large, especially the phase influence is large. If the design is not good, the sound will be messed up. So the higher the crossover, the better. The 2.0 multimedia speakers on the market, mostly using capacitance or RC, use very few dividers and use second-order divisions. For example, the shock wave SB-2000 uses a first-order frequency divider, while the second-order frequency division uses only the Swans T200A, M200, the Rambler S2000, 1900TIII, etc.