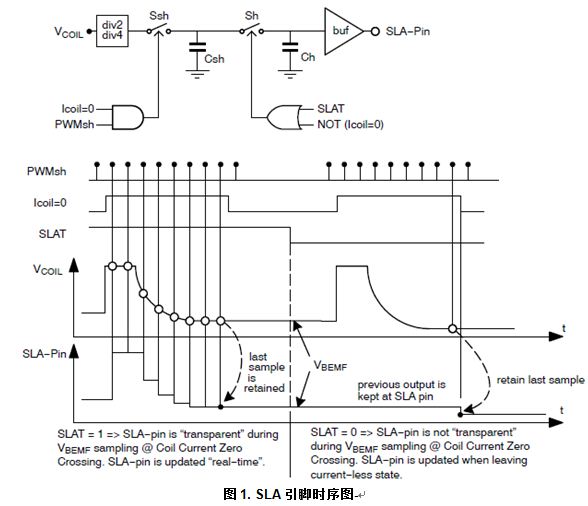
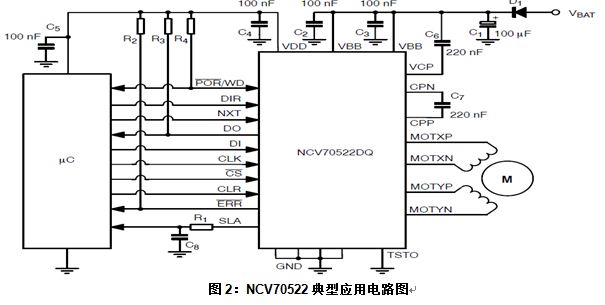
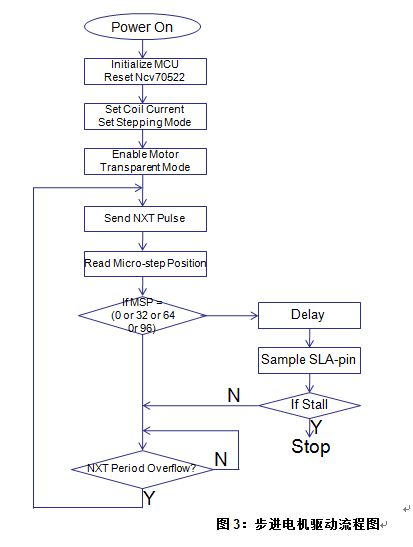
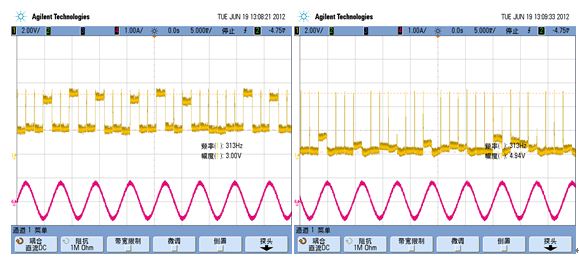
Introduction This article refers to the address: http:// Due to mechanical limitations, stepper motors can sometimes stall during adaptive headlamp system (AFS) applications. Once the motor is stalled, the electronic control unit (ECU) will lose track of the headlamp position and react inappropriately, creating a very serious safety problem, so stall detection is essential in AFS applications. It is usually possible to judge whether the motor is blocked or not by the back electromotive force ( BEMF ) of the motor. BEMF varies depending on motor speed, load and supply voltage. The traditional stepper motor driver chip has no BEMF output, but includes a built-in stall detection algorithm. The customer can only set a fixed stall determination threshold in the register, which means that under real road conditions all settings must be “offline†preset before work, and cannot be adapted to real working conditions. Semiconductor NCV70522 stepper motor micro-step driver provides an output through SLA BEMF pin, which means that it can calculate in real time stall detection, and the detection level is adjusted depending on the conditions. Algorithm description Since the recirculating current during coil current decay is relatively large, the coil voltage Vcoil exhibits transient characteristics. Since the application software does not always want transients, you can pass To adapt the sampled BEMF output level to the (0 V to 5 V) range, the sampled coil voltage Vcoil can optionally be divided by 2 or 4. This setting is via the SPI bit. This BEMF voltage is sampled during each so-called "coil current zero crossing". Each coil has two zero current positions in each electrical cycle, so there are four zero-crossing observation points per electrical cycle, so four BEMFs can be measured. If the microstep position is at "coil current zero crossing", the BEMF voltage will only be sampled by the motor driver. The microstep position can be read via the SPI interface. Through software, we can flexibly determine whether to stall based on the measured 4 SLA values ​​in one electrical cycle. Algorithm application The NCV70522 is a microstepping stepper motor driver for bipolar stepper motors. The chip is connected to an external microcontroller via an I/O pin and an SPI interface. The NCV70522 has a variety of output currents. It rotates the next microstep based on the pulse signal on the “NXT†input pin and the state of the direction register [DIRCTRL] or “DIR†input pin. The device provides subdivision from full steps to 32 microsteps and seven step modes selected by the SPI register SM[2:0]. The NCV70522 contains the output of the SLA and can be used for stall detection algorithms and for adjusting torque and speed calculations based on the BEMF of the motor. A typical application circuit diagram is shown in Figure 2. When the system is powered up, the microcontroller is initialized and the NCV70522 is reset. When these actions are completed, the coil current and step mode will be set. Then the motor drive will be enabled. The NXT pulse will be sent to implement the rotating motor. The motor speed is equal to the NXT pulse frequency multiplied by the value of the step subdivision mode. Figure 3 is a flow chart. Example: Check the SLA output level during normal and stalled states as follows: Therefore, we can think that if there are 2 SLA levels below 4 V in 4 "coil current overcurrent points", then it is in a stalled state. Introduction Compared with the traditional stepper motor driver IC, the NCV70522 includes BEMF output, which can accurately reflect the motor operation in real time, which is very suitable for applications in automotive adaptive headlamp systems. The stall detection threshold can be adjusted according to the motor speed, load characteristics and supply voltage. Shenzhen Ever-smart Sensor Technology Co., LTD , https://www.fluhandy.com