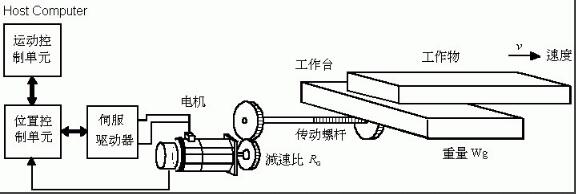
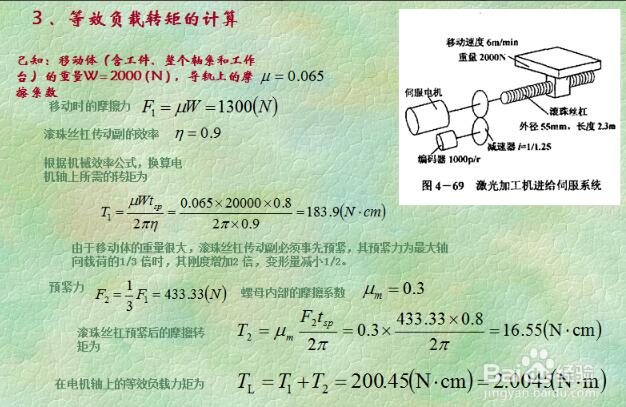
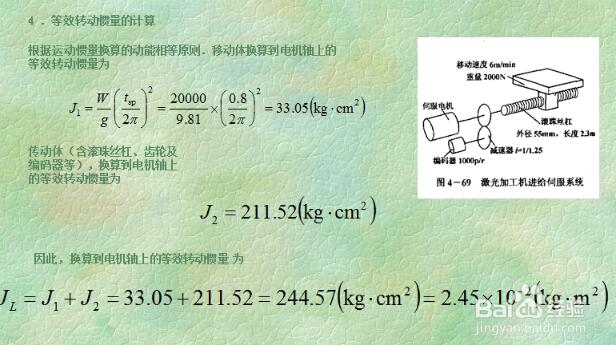
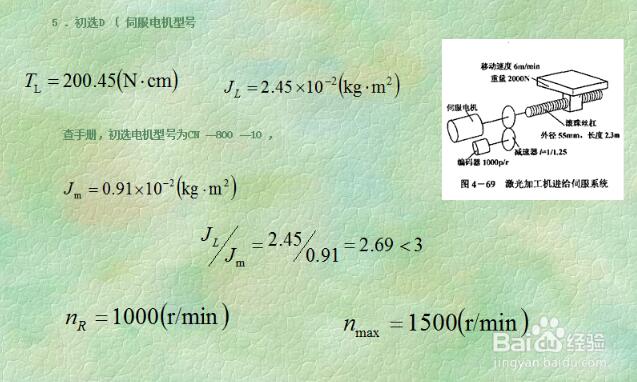
In order to meet the requirements of high precision and fast response of mechanical equipment, the servo motor should have a small moment of inertia and a large locked rotor torque, and have as small a time constant and starting voltage as possible, and should also have a long time overload. Capability, to meet the requirements of low speed and large torque, able to withstand frequent starting, braking and positive and negative, if blindly choose a large size motor, not only increase the cost, but also increase the size of the design equipment, the structure is not compact, Therefore, the selection of the motor should fully consider the requirements of all aspects, in order to give full play to the working performance of the servo motor; the following describes the selection principle and precautions of the servo motor. 1. Defining the requirements of the motion conditions of the load mechanism, namely the speed of acceleration/deceleration, the speed of movement, the weight of the mechanism, and the movement mode of the mechanism. 2. According to the operating conditions, select the appropriate load habit calculation formula to calculate the load inertia of the mechanism. 3. Select the appropriate false selected motor specifications based on the load inertia and motor inertia. 4. Calculate the acceleration torque and deceleration torque in combination with the primary motor inertia and load inertia. 5. Calculate the load torque according to the load weight, configuration mode, friction coefficient and operating efficiency. 6. The maximum output torque of the primary motor must be greater than the acceleration torque plus load torque; if the conditions are not met, other models must be used for verification until the requirements are met. 7. Calculate the continuous instantaneous torque based on the load torque, acceleration torque, deceleration torque and holding torque. 8. The rated torque of the primary motor must be greater than the continuous instantaneous torque. If the condition is not met, other models must be used for verification until it meets the requirements. 9. Complete the selection. 1. Confirmation of speed and encoder resolution. 2. Calculation of load torque on the motor shaft and calculation of acceleration and deceleration torque. 3. Calculate the load inertia and the inertia match. For example, the Yaskawa servo motor can match the inertia of some products up to 50 times, but the actual smaller the better, so the accuracy and response speed are good. 4, the calculation and selection of regenerative resistors, for the servo, generally 2kw or more, to be configured outside. 5, cable selection, encoder cable twisted shield, for the Yaskawa servo and other Japanese products absolute encoder is 6 core, incremental is 4 core. The above selection method only considers the dynamic problem of the motor. For the linear motion speed, the acceleration and the required external force, for the angular velocity of the rotational motion, the angular acceleration and the required torque, they can all be expressed as a function of time, and other Factors have nothing to do. obviously. The maximum power P motor of the motor should be greater than the peak power P peak required for the working load, but this is not enough. The physical power includes both torque and speed, but they are limited in the actual transmission. of. With the peak value, the T peak indicates the maximum value or the peak value. The maximum speed of the motor determines the upper limit of the reduction ratio of the reducer. n upper limit = peak value, maximum / peak value. Similarly, the maximum torque of the motor determines the lower limit of the reduction ratio. The lower limit of n = T peak / T motor, the maximum, if the lower limit of n is greater than n upper limit, the selected motor is not suitable. Conversely, a range of possible gear ratios between the upper and lower limits can be determined by a broad analogy for each type of motor. The principle of using only peak power as the motor of choice is not sufficient, and the accurate calculation of the gear ratio is very cumbersome. 1. First of all, you need to distinguish common motors, such as servo motors, spindle motors, and asynchronous motors. You must clearly understand why servo motors are used. Servo motors are generally used in CNC systems. It is controllable and can achieve semi-closed loop control. And closed loop control. 2, our commonly used servo motor manufacturers are Siemens, FANUC FANUC, and some other manufacturers, but the selection process is similar, the following is a Siemens selection as an example. 3. First, the load torque needs to be calculated. The calculation of the load torque requires calculation of the load force. The load force may be friction or cutting force. A rough calculation should be made according to your mechanical system. The unit of load torque is NM. Therefore, the rotational diameter (radius) of the workpiece is also known. 4. Then calculate the moment of inertia of the workpiece according to the rotational speed of the workpiece and the mass of the load. Then, the load torque and moment of inertia of the workpiece need to be converted into the moment of inertia and load torque of the spindle. 5. After obtaining the above torque and moment of inertia, you can contact the manufacturer to determine the motor used. The selection of the servo motor generally does not look at the speed. One principle is that the rated torque of the selected motor is ×0.8 than the motor that is converted to the motor shaft load torque, TMx0.8>TL. Moment of inertia: The motor with the rotor and inertia of the selected motor is 1/3* or more of the load: JM≥JL/3. 6. Finally, you need to determine some fine details, such as the output shaft of the motor, the key, the brakes, the protection level, the coding system, and so on. Recommend a software: CAD CREATOR 2.0, can be downloaded from the official website of Siemens, can help you choose. And the drawings and models of the corresponding motors are everywhere. 1. Select the load inertia calculation formula according to the operation requirements and calculate the load inertia of the mechanism. 2. Generally, the requirements of the motion conditions of the load mechanism, that is, the acceleration and deceleration speed, the running speed, the weight, the operation mode, etc., are necessary, which is necessary to select the servo specifications. 3. Load weight, configuration mode, and friction coefficient to calculate load torque. 4. Load inertia and servo motor inertia are also necessary considerations for selecting the motor specifications. The user can calculate the acceleration torque and deceleration torque according to the two, and select the false selection specifications. 5. Load torque, acceleration/deceleration torque, and holding torque, and calculate continuous instantaneous torque. The continuous instantaneous torque must be less than the rated torque of the primary servo motor. Otherwise, other qualified specifications can only be selected. 6, pay attention to acceleration torque + load torque <maximum output torque of primary servo 1. Some systems, such as conveyors, lifting devices, etc., require the servo motor to stop as soon as possible. In the event of a fault, an emergency stop, or a power failure, the servo is not regeneratively braked and cannot decelerate the motor. At the same time, the mechanical inertia of the system is large. At this time, the dynamic brake should be selected according to the weight of the load and the working speed of the motor. 2. Some systems need to maintain the static position of the mechanical device, and the motor needs to provide a large output torque, and the stopping time is longer. If the self-locking function of the servo is used, it will often cause the motor to overheat or the amplifier to be overloaded. In this case, the motor with electromagnetic brake should be selected. 3. Some servo drives have a built-in regenerative braking unit. However, when the regenerative braking is frequent, the DC bus voltage may be too high. In this case, a regenerative braking resistor is required. Whether the regenerative braking resistor needs to be equipped separately, and how big it is, can refer to the instructions for use of the corresponding sample. 4. If a servo motor with an electromagnetic brake is selected, the moment of inertia of the motor will increase, and consideration should be given when calculating the torque. Led Floor Panels,Led Dance Floor Panel,48W Led Light Panel,Floor White Uplight Panel Led Kindwin Technology (H.K.) Limited , https://www.ktlleds.com