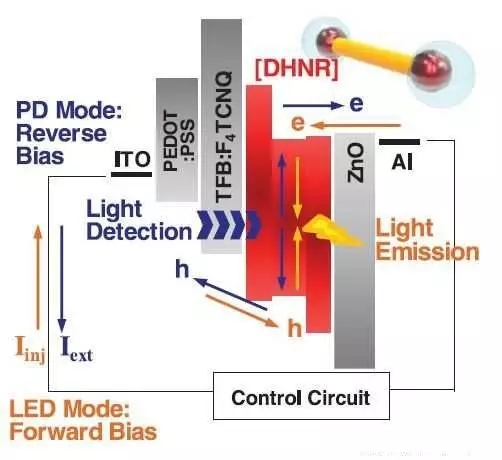
Recently, an international research team composed of researchers from the United States and South Korea has released a new type of nanoLED with an unprecedented brightness level (over 80,000 cd/m2) that can be used simultaneously as a light emitter and photodetector. The research, published in the journal Science, predicts that dual-mode LEDs can enable new interactive displays in the article "Double Heterojunction Nano-Bar Light-Responsive LEDs for Display Applications." This fully solution treated double heterojunction nanorod (DHNR) photoresponsive LED comprises quantum dots that directly contact two different semiconductor materials in a nanorod. In this configuration, the quantum dots are either biased according to the voltage to enhance the radiation recombination (facilitating the LED) or to cause efficient separation of the photogenerated carriers. The layered structures in these anisotropic nanorods can be individually adjusted to fine tune recombination and charge separation in a single assembly, thereby enabling a single nanorod to electroluminescence and produce photocurrent. Once the nanorods are properly stacked between the two electrodes, the nanorods can be configured to switch between the illumination mode and the photodetection mode by simply changing the voltage offset (forward or reverse). . The component is said to have a low turn-on voltage (about 1.7V) and a maximum brightness of over 80,000 cd/m 2 and exhibit low bias and high efficiency in display-related brightness. The researchers also released the component to support 8.0% external quantum efficiency at a luminance of 1000 cd/m2 at 2.5V bias. But in another experiment, the researchers operated a 10×10 pixel DHNR-LED array as a live photodetector (in reverse), combined with a forward bias to detect any incident on any pixel. Light board. DHNR-LED energy band diagram and charge emission direction of light emission (orange arrow) and detection (blue arrow), and DHNR schematic By alternating forward and reverse biases in sub-millisecond time, they are able to "read" the light to detect pixels continuously while illuminating the array. The experiment led the researchers to believe that several new display features can be easily implemented by integrating a simple control circuit to convert any detected signal into a brightness adjustment. For example, the brightness can be automatically adjusted in response to changes in external light intensity. However, since light detection can be performed at the pixel level, the shadow on the screen is compensated, or the finger is detected to be approached and interpreted as a new touch-free command. The researchers imagined the single pixel sensing capability of the DHNR-LED and also supported direct imaging or scanning of the screen. Another possible application of the DHNR-LED dual illumination and light detection mode of operation is to convert a tightly coupled LED display (actually a large array of nanoLEDs) into a large-scale parallel data communication and processing component that performs direct data from the display-display. communication. In addition, the light detection in the DHNR photoresponsive LED is similar to the photoelectric (PV) effect, and the display can capture or remove energy from the ambient light source without the need to integrate separate solar cells, making the display more efficient. The last use case in the research theory also demonstrated in experiments that LEDs can be coupled to supercapacitors. Moonsub Shim, a professor at the University of Illinois, who led the study, said, "We have partnered with Dow Chemical to apply for a patent for this technology, so there will be some commercial benefits in the future." Cat Litter Box,Cat Star Box,Covered Cat Litter Box,Appearance Cat Litter Box Sensen Group Co., Ltd.  , https://www.sunsunglobal.com