In recent years, the construction speed of photovoltaic power stations in China has been very fast, but the supporting construction is still unable to keep up. In addition, the ability to absorb photovoltaic power in the western region is limited. For example, in Gansu, Xinjiang, Qinghai and other places, many photovoltaic power plants have experienced power limitation problems. The dilemma has brought huge energy waste. The proportion of power cuts in some months has reached 90%. The investment yield of photovoltaic power plants has been greatly reduced, and it is also very unfavorable for the future development of photovoltaics. It is necessary to strengthen the construction of supporting power grids. Photovoltaic power is sent to areas with strong capacity for consumption, or the contradiction arising from competition for energy interests such as thermal power, photovoltaics, and wind power is improved, and the energy structure is further adjusted to give priority to the use of photovoltaic power.
As the country's ecological environment and climate change situation become increasingly severe, the energy revolution characterized by priority in the development of renewable energy has become an inevitable trend. This paper takes the power-limited situation of a power station in Gansu as an example, and briefly introduces the calculation method and technical countermeasures of power generation loss caused by power-limiting.
1. Active Power Control System (AGC)
The photovoltaic power station's power limitation is inseparable from the photovoltaic active power control system (AGC). In May 2011, the State Grid Corporation issued the "Technical Regulations for Connecting PV Power Plants to the Power Grid", stating: "Photovoltaic power plants should have active power regulation capabilities, capable of Receive and automatically execute the control commands of the dispatching department to ensure that the active power and active power changes operate according to the requirements of the dispatching department." Therefore, large-scale photovoltaic power plants are required to be equipped with photovoltaic active power control systems, receive active power control commands from the dispatch center, and achieve load distribution according to predetermined rules and strategies.
In general, the AGC control mode can be divided into two types: plan curve and fixed value control. Figure 1 shows the fixed value tracking mode, that is, the total output power of the control station on the same day is a constant value, which depends on the provincial adjustment. When the sunny day irradiation is good, if the real-time power output value exceeds the limit value, Will be "shaved", then the real-time curve looks close to the trapezoidal curve.
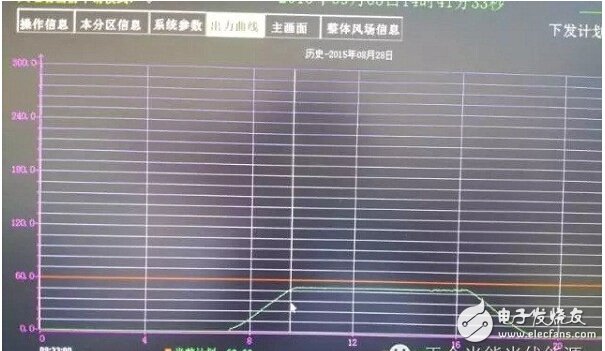
Figure 1 AGC limited power value tracking mode (provincially limited load 60MW)
Figure 2 shows the plan curve tracking mode. The general power-off time is a certain period of time, and there is no regularity, such as 14 to 16 pm, so that the total active power curve (red) stays up and down around the defined target curve (green), and The minimum tolerated fluctuation range for each region will vary, as above floating below no more than 0.3 MW or 0.5 MW.

Figure 2 AGC plan curve tracking mode
Incremental encoders provide speed, direction and relative position feedback by generating a stream of binary pulses proportional to the rotation of a motor or driven shaft. Lander offers both optical and magnetic incremental encoders in 4 mounting options: shafted with coupling, hollow-shaft, hub-shaft or bearingless. Single channel incremental encoders can measure speed which dual channel or quadrature encoders (AB) can interpret direction based on the phase relationship between the 2 channels. Indexed quadrature encoders (ABZ) are also available for homing location are startup.
Incremental Encoder,6Mm Solid Shaft Encoder,Hollow Rotary Encoder,Elevator Door Encoder
Jilin Lander Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.jilinlandermotor.com