1 Introduction In the past ten years, most enterprises have invested almost astronomically in IT systems. Vendors are using their own IT technology to develop suitable application systems for different departments within the enterprise every day. For example, for the sales department, accounting department or human resources department, marketing department, R & D department and even the logistics department, each department has its own unique application to maintain its own operations. Every department manager believes that these systems are ensuring their competitiveness. However, with the passage of time, various self-relatively independent application systems that have emerged have brought huge challenges to IT management. Users begin to integrate and manage programs through various methods including: manual processing, formulating processes, and even adding programs layer by layer on top of each system. Hope to establish a complete IT environment through these methods. But the conclusion is that the process of this implementation is very expensive, and it forms an application environment that is constantly changing and the efficiency of the entire IT operation is reduced. The continuous exposure of problems has caused the company's attitude to IT management to change drastically. Enterprise decision-makers have begun to recognize the establishment of a long-term goal and strategy that can achieve cost reduction through automation and process reengineering. The emergence of cloud computing has largely solved the above problems. Cloud computing architecture is a cost-effective model for providing information services, reducing IT management complexity, promoting innovation, and improving responsiveness through real-time workload balancing. It can quickly publish applications and expand applications on demand, making it possible to instantly expand applications on thousands of servers. But there are also huge risks for companies to implement private clouds, that is, IT expenditures are only transferred from hardware to operations, rather than achieving the desired overall expenditure reduction. Other issues, such as always following standard processes, achieving scalability, and maintaining compliance, often challenge customers who often only achieve such operational maturity in their specific IT operations. Therefore, we need to bring the strictness of service management to cloud computing in order to effectively neutralize these risks and ensure that customers can safely and economically execute strategic operations plans. 2 Cloud Computing Overview Cloud computing is the development of parallel computing (Parallel CompuTIng), distributed computing (Distributed CompuTIng) and grid computing (GridCompuTIng), or the commercial realization of these computer science concepts. 2.1 Definition of cloud computing Cloud computing does not yet have a unified standard definition, and some large companies have given their own definitions in their technical documents. For example, cloud computing defines the definition of cloud computing in IBM's documents: The term cloud computing is used to describe a system platform or a type of application. A cloud computing platform dynamically deploys, configures, reconfigures, and revokes services as needed. From the perspective of an enterprise's private cloud, cloud computing is to distribute computing on a large number of distributed computers instead of local computers or remote servers. The operation of enterprise data centers will be more similar to the Internet. This allows companies to switch resources to the applications they need and access computers and storage systems as needed. 2.2 Features of Cloud Computing Super large scale: "Cloud" has a considerable scale, Google Cloud Computing already has more than 1 million servers. Enterprise private clouds generally have hundreds or thousands of servers. "Cloud" can give users unprecedented computing power. Virtualization: Cloud computing supports users to obtain application services at any location and using various terminals. The requested resource comes from. "Cloud", not a fixed tangible entity. The application runs somewhere in the "Cloud", but in fact users do not need to know or worry about the specific location of the application. Only a laptop or a mobile phone is needed to achieve everything we need through network services, even tasks such as super computing, to meet the freedom of enterprise employees to work. High reliability: "Cloud" uses multiple data copy fault tolerance, computing node isomorphic interchangeability and other measures to ensure high reliability of services. Using cloud computing is more reliable than using local computers. Versatility: Cloud computing is not aimed at specific applications. Under the support of "cloud", it is possible to construct ever-changing applications, the same one. "Cloud" can support different applications at the same time. High scalability: The scale of the "cloud" can be dynamically scaled to meet the needs of application and user scale growth. Extremely cheap: Due to the special fault-tolerant measures of "cloud", extremely inexpensive nodes can be used to form the cloud. The automated centralized management of "cloud" eliminates the need for large enterprises to bear the costly data center management costs. Compared with traditional systems, the utilization rate of resources has been greatly improved. 2.3 Cloud computing architecture Cloud computing is a virtualized computer resource pool and a new mode of IT resource provision. It provides data, applications and other resources to users through the network as a service. It includes a data center. The computers in this data center can manage and dynamically allocate, deploy, configure, redistribute, and reclaim resources. The composition of the data center includes hardware, software, and other essential resources. Cloud computing users include two parts. One is the end user, who directly uses various resources provided by the data center. The other is a component or service provider. When they use data center resources, they are also publishing their own components or services to the data center. 3 ITIL overview The actual standard and best practice guide for a type of IT service management that is commonly used in the industry is ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library), which is the information technology infrastructure library. 3.1 ITIL framework ITIL is a set of IT service management standard libraries developed by CCTA (British National Computer and Telecommunications Authority) in the late 1980s. It summarizes the best practices of IT management in various industries in the UK into specifications, including how to manage IT infrastructure process description: It takes the process as the guide and the customer as the center. Through the integration of IT services and enterprise services, it improves the ability and level of enterprise IT service provision and service support. ITIL can guide organizations to use technology efficiently and effectively, so that existing information resources can play a greater role. ITIL V3.0 is the latest version evolved from the changes in the current IT service management market. It is a brand-new ITIL framework proposed from the perspective of IT serving enterprise business services, mainly based on the best practices of service lifecycle management. ITIL V3.0 from the three levels of strategy, tactics and operation, according to the characteristics of rapid changes in business and IT, all IT service management Good practice is reorganized according to the life cycle, and IT service management is divided into five core parts: service strategy, service design, service execution, service operation and continuous service improvement. The five parts are closely related to each other. ITIL V3.0 carries out service design, conversion, on-line operation and improvement based on strategy. According to the cycle of PDCA (Plan—Do—Check—Act), it forms the life cycle of ITSM implementation. In the service strategy stage for actual decision-making, V3.0 defines the role and requirements of IT, ensuring the success of the entire business. In the service design stage of planning the actual service blueprint, V3.0 requires the design of IT services to make it Can meet the needs of enterprise functions and performance, at the same time with manageability and cost-effectiveness; in the service conversion stage, V3.0 requires testing services. And introduce it into the infrastructure in a controlled manner to improve management changes, reduce risks, and ensure quality; in the service implementation stage, V3.0 requires the provision of real services and support for services, improving service stability and responsiveness: in the application In the continuous service improvement phase of service measurement, V3.0 requires continuous monitoring of the quality and cost of service determination methods to reduce their costs and keep them consistent with changing business needs. 3.2 ITIL implementation framework The implementation of IT service management is a process of continuous service improvement. As the de facto international standard for IT service management, ITIL defines a strict logical relationship between various processes, providing us with a "best practice" guide. The ITIL implementation framework provides us with a reference model for top-down planning and bottom-up implementation, and recommends an order for implementing service management processes. ITIL must proceed from two directions. The plan should be planned from top to bottom, and the realization should be from bottom to top. As shown in Figure 3. The operation layer, including the service support process of IT services, is mainly for end users. It is responsible for ensuring the stability and flexibility of IT services, and is used to ensure that end users receive appropriate services to support the business functions of the organization. The service support process includes service desk intelligence and five processes that reflect service contact and communication. The main function of these five processes is to ensure that the quality of service provided by the service provider meets the requirements of the service level agreement (SLA). The tactical layer, which includes the service delivery process of IT services. Its main task is to plan and design service level objectives such as service capability, continuity, and availability according to the business needs of the organization. . ITIL only stipulates what is correct in IT operation and maintenance, and those things should be done, but it does not clearly explain how to do these things and how to implement these theories in the enterprise. 4 ITIL-based cloud computing implementation strategy (1) IT service strategy. Business analysis and IT strategic planning. The first thing an enterprise IT management must do is to analyze the current IT resource status of the enterprise, formulate an IT governance framework and evaluate it. For an enterprise, the goal of ITIL is to find applications that meet the real needs of the enterprise at an acceptable cost and provide high-quality and most suitable services. Therefore, ITIL can be partially adopted, so our first step Find out the IT management process suitable for the current enterprise. (2) IT service design. Strictly implement the established IT management process and transform enterprise IT resources, that is, build a cloud computing infrastructure. The basic steps are as follows: ② Flexible expansion of dynamic resources. As the cloud computing business progresses, cloud computing resource requirements will continue to change, so the cloud computing center needs to achieve flexible expansion of resources (which can include resources outside the enterprise) and dynamically and intelligently allocate environmental resources. ③ Application transformation business innovation. Develop and deploy new application services under the premise of the lowest cost and process, the most effective, and the most stable and feasible flexible expansion. This link requires the transformation and coordination of the company's organizational structure to improve the consistency of IT and business. This step is to realize the value of cloud computing to meet the needs of business innovation and provide more services for enterprises. (3) IT services perform a configuration management. Maintaining accurate, consistent, and reliable infrastructure information is of particular importance for the successful execution and operation of services. Configuration management is to manage and provide accurate and reliable cloud infrastructure configuration information in a timely manner, so that the services provided by the cloud have effective resources. The implementation of configuration management can quickly understand the impact of changes, and implement changes more quickly and effectively. It is an indispensable key for IT service management implementation. (4) IT service operates a service desk. The service desk plays a key role in the overall IT service management. The service desk is customer-centric and consists of technical experts, business backbones, and people with strong coordination capabilities. It provides high-quality support services to achieve business goals, reduces the overall cost of providing and using IT services, improves user satisfaction, and assists in discovery. Business opportunities, optimization of investment and management of support services, and support for comprehensive changes in business, processes and technology. The daily activities of the service desk include requirements management, reporting, review and feedback. (5) Continuous service improvement. Service supervision, evaluation and improvement. IT services can only be achieved through continuous service evaluation and improvement. Keeping up with the times "adapting to changes in demand is invincible. The user requests the service cloud through the user interaction interface. All service catalogs that a user can request are stored in the service catalog. System management is the center of the management system, which is equivalent to a help desk. It is responsible for recording, forwarding, tracking, and feedback of events submitted by different channels to provide support for the operation of IT services. Configuration management is used to process the requested service and deploy the service configuration. The monitoring statistics are used to track and measure user services, submit them to the central server, and then the service desk feeds them back to the cloud computing center for service improvement. Unified management of cloud computing architecture through the above mechanism. 5 Summary and outlook This article mainly introduces the principles and architecture of cloud computing, as well as the ITIL implementation framework, and on this basis, proposes cloud computing implementation steps that comply with ITIL standards to solve the growing IT management problems of enterprises. The implementation of enterprise cloud computing combined with the ITIL concept, in line with the IT management model, is also more easily accepted by people, so it will inevitably receive more and more attention. In other words, configuration item management is the basis of change management, and its quality has a direct impact on the effectiveness of change management implementation.
The LED projector lamp is used to specify the luminance above the surrounding environment, and also called the spotlight.Usually, it can be aimed at any direction and has a structure that is not affected by climatic conditions.It is mainly used for large area operation field, building outline, stadium, overpass, monument, park and flower bed.As a result, almost all outdoor use of large areas of lighting can be seen as a projector lamp.
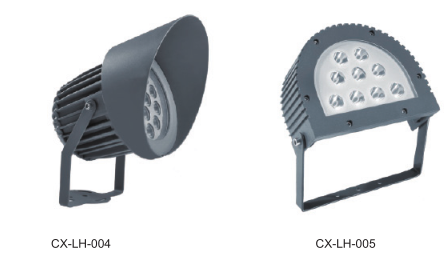
Description of products
1. Fashionable, modern appearance design, make lamps and lanterns also become a work of art, with the environment perfect union.
2. The main material of the luminaire is made of high strength die-casting aluminum material, and the surface anti-aging electrostatic spraying process, Self-cleaning and anti-corrosive.
3. Tempered glass cover with high strength and impact resistance.
4. The lamp can be configured white or monochromatic RGB, gorgeous lighting effects, color purity, powerful change.
5. The lamp body is made of high - die cast aluminum material, surface electrostatic spraying
6. The unique rotatable fixed bolt can be rotated 360 degrees.
7. The light source adopts 1W single RGB light source, LED combination optical arrangement, and the mixing effect is better.
8. The light can be controlled by DMX512, a powerful function of changes in lighting effects.
9.Lamp series, power can be between 18W-36W, can be used for a variety of applications.
Product show
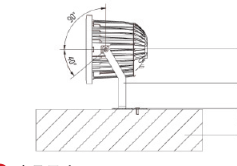
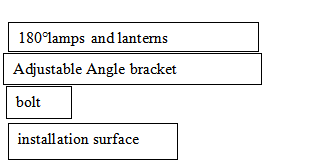
Installation Instruction
Led Tile Slots Lamp,Led Project Lamp,Led Night Lamp,Led Mood Lamp Jiangsu chengxu Electric Group Co., Ltd , http://www.chengxulighting.com
â‘ Realize automatic deployment. Target those IT areas that are manual, repetitive, error-prone, and expensive. Look for opportunities for automation in those repetitive, manual tasks, and determine that these tasks are unplanned, error-prone, and time-consuming to execute. By automating these functions, companies will significantly benefit from reducing costs and improving service quality.